Fig. 9.
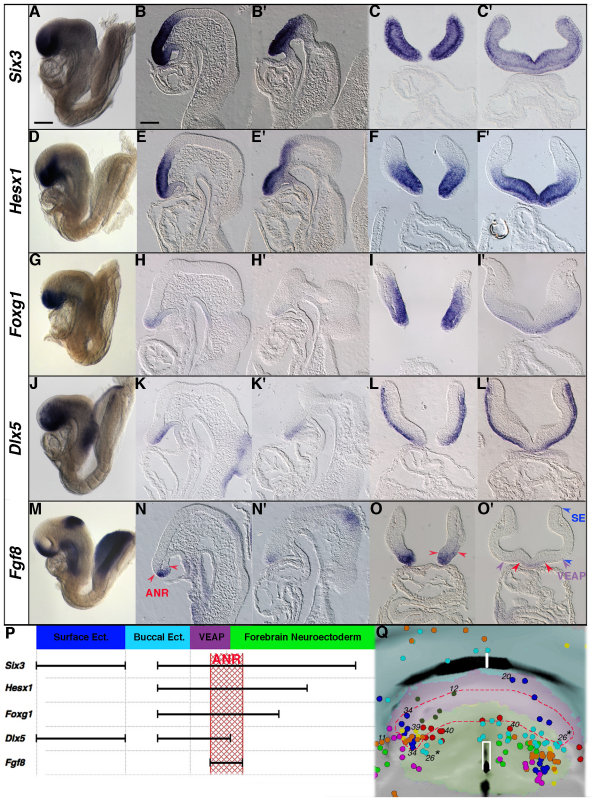
Molecular analysis of the non-neural and neural tissues forming the rostral end of the head. (A-O′) Whole-mount (A,D,G,J,M), parasagittal (B,E,H,K,N), sagittal (B′,E′,H′,K′,N′) and frontal (C,C′,F,F′,I,I′,L,L′,O,O′) histological sections of 5- to 7-somite stage embryos. (A-C′) Six3 is strongly expressed throughout the forebrain neuroectoderm, the VEAP, the buccal ectoderm and the surface ectoderm. (D-F′) Hesx1 is strongly expressed in the forebrain but weakly in the VEAP and the buccal ectoderm. (G-I′) Foxg1 is expressed in the forebrain, the VEAP and the buccal ectoderm. (J-L′) Dlx5 is expressed in the VEAP, the buccal ectoderm and the surface ectoderm. (M-O′) Fgf8 expression is found in the anterior neural ridge (ANR) and the isthmus at the midbrain-hindbrain level, in the buccal ectoderm at the level of the oral plate and in the foregut endoderm. The red arrowheads point to the boundary of the ANR as defined by Fgf8 expression domain. (O′) Purple and blue arrowheads delimit the VEAP and the surface ectoderm (SE) laterally. Note that Six3, Hesx1 Foxg1 and Dlx5 are expressed in the rostral portion of the buccal ectoderm (anterior to the oral plate). (P) Linear representation of the gene expression profiles and their overlapping domains at the 7-somite stage. The relative extent of the expression domains (black bars) estimated on histological sections is conserved, except for the surface ectoderm. The Fgf8 expression domain defines the ANR (hatched red box) encompassing part of the forebrain neuroectodem and the rostral part of the VEAP. (Q) The contribution of forebrain and VEAP clones to the ANR. The red dashed line encloses the fitted positions of the HRP-labelled cells scored as contributing to the ANR. Asterisks indicate that one clone originated from two siblings. Scale bars: 110 μm in A for whole-mount images; 60 μm in B for histological sections.