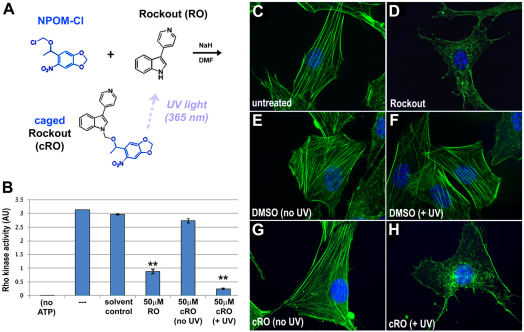
Fig. 1.
Synthesis of a photoactivatable Rho kinase inhibitor. (A) Caged Rockout (cRO) was generated by installing 6-nitropiperonyloxymethyl (NPOM) on the indole nitrogen of Rockout (RO). Exposure to UV light releases the NPOM caging group, restoring Rho kinase inhibitory activity. (B) Rho kinase activity was assayed in vitro using a Rho kinase assay, under standard conditions (---) or in the presence of DMSO (solvent control), 50 μM RO, or 50 μM cRO with (+ UV) and without (no UV) irradiation. The assay was also run without ATP as a negative control (no ATP). The data shown are representative of several independent trials; in the trial shown, the effect of cRO + UV is slightly greater than the effect of RO itself (P<0.05), but this result was not consistently observed. **, P<0.01 (one-way ANOVA); error bars indicate s.d. (C-H) NIH3T3 cells were untreated (C) or exposed to RO (D), DMSO (E,F) or cRO (G,H) and left in the dark (C-E,G) or exposed to UV irradiation (F,H). Blue, DAPI; green, phalloidin.