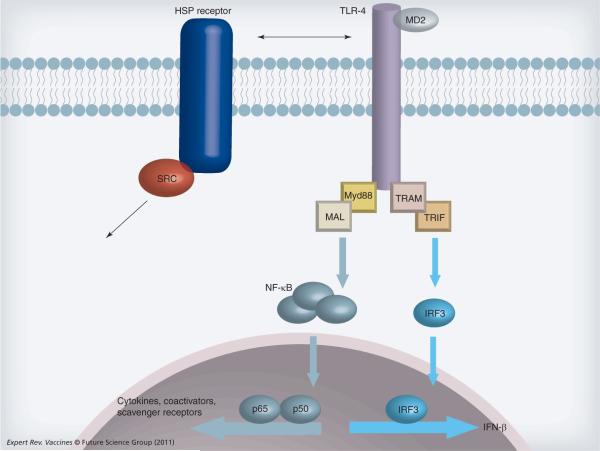
Figure 3. Heat shock protein receptors and Toll-like receptor 4 signaling.
TLR-4 (and other TLR family members) can be activated in antigen-presenting cells and other immune cells by extracellular HSP either directly or indirectly through a primary receptor such as SREC-I or LOX-1. Ligand binding then triggers the complex TLR signaling cascade. We show a highly simplified cartoon. Ligand-activated TLR-4 engages a range of intracellular adaptor proteins (Myd88, TRAM, MAL, TRIF shown here) that regulate the various arms of TLR-4 signaling. Here we show activation of transcription factors NF-κB and IRF3. NF-κB complex proteins p65 and p50 can bind the promoters of cytokine genes, co-activators and scavenger receptors to modulate the phenotype of the antigen-presenting cell and influence other cells through receptor expression and cytokine signaling. TLR-4 activation can influence other transcriptional events such as activation of IFN-β through IRF3.
HSP: Heat shock protein; IRF: Interferon regulatory factor; TLR: Toll-like receptor.