Figure 7.
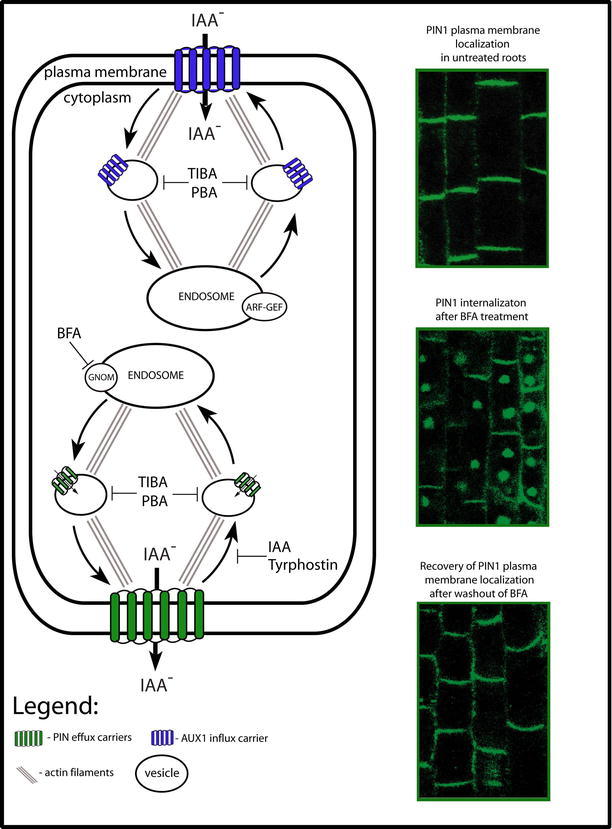
The subcellular dynamics of efflux (PINs) and influx (AUX1) carriers. This diagram illustrates a model for constitutive cycling of PIN and AUX1 proteins. Included are images of PIN1 subcellular localization (by immunolocalization). The constitutive cycling of PIN proteins between the endosomes and the plasma membrane (PM) is actin-dependent. BFA blocks the exocytosis of PINs by inhibiting GNOM, the ARF-GEF required for the vesicle budding at endosomes. This leads to the internalization of PINs into so called "BFA compartments." Endocytosis of PIN proteins is not affected by BFA, but is sensitive to clathrin pathway inhibitor Tyrphostin and IAA. Auxin efflux inhibitors such as TIBA or PBA interfere with both steps of PIN protein cycling. AUX1 also cycles constitutively between the endosomes and the PM along actin cytoskeleton. Although, AUX1 dynamics is sensitive to BFA treatment, its exocytosis is largely BFA-insensitive. TIBA and PBA interfere also with AUX1 cycling.
