Figure 29.
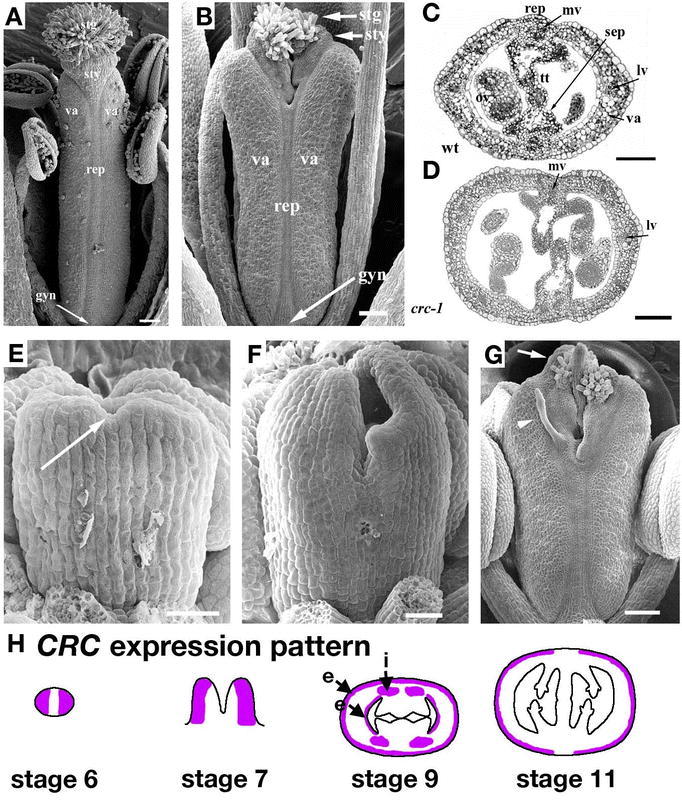
CRABS CLAW is necessary for apical fusion of the carpels. (A) Wild-type gynoecium at stage 13. (B) crc mutant at stage 13. Note the unfused style and upper ovary. (C) Cross-section through a wild-type gynoecium at stage 13. (D) Cross-section through a crc gynoecium at stage 13 showing the unfused septum. (E) A cleft (arrow) begins to form in the medial regions of a stage 6 crc gynoecium. (F) Stage 10 crc gynoecium where the cleft has deepened and the tips of the carpels where the stigma will form are starting to turn inward. (G) Late stage 12 crc gynoecium where the two halves of the stigmatic surface are curved inward and the stigmatic papillae are interlocking. An aberrant ovule primordium has arisen on the outside of the replum (arrowhead). (H) Based on in situ hybridization results, CRC is expressed in the lateral sides of the gynoecium at stage 6 and stage 7. At stage 8, CRC is expressed in two domains. The epidermal (e) domain includes both the outer and inner epidermis of the carpels. The internal (i) domain includes 4 spots near the placentas. By stage 11, CRC is expressed only in the outer epidermis of the valves and not the replum or the internal domains. Scale bars on A-D represent 100 µm, E-F represent 25 µm, and G represents 50 µm. A-G: from Alvarez and Smyth, 2002.
