Figure 11.
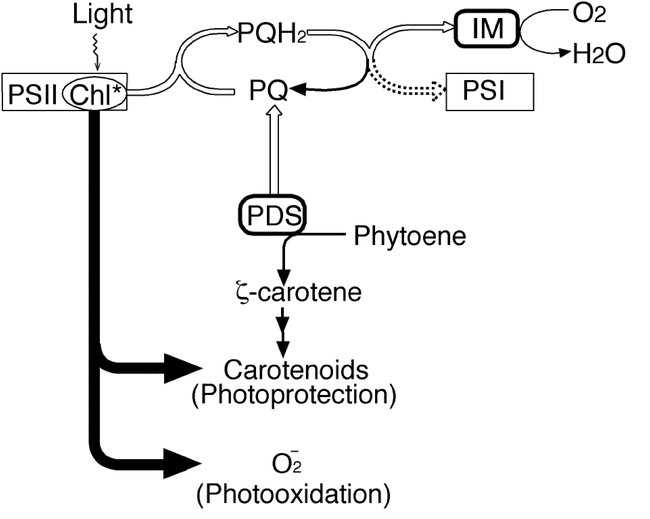
Working model of immutans variegation.Light is absorbed by the light harvesting complex of photosystem II (PSII), and energy from excited state chlorophyll can either be transferred to the reaction center or be used to form triplet chlorophyll. Unless quenched by colored carotenoids, energy from triplet chlorophyll generates oxygen radicals (O2−), which can lead to the photooxidation of the contents of the plastid if not detoxified by free radical scavengers (such as superoxide dismutase). The pathway of energy flow from triplet chlorophyll is indicated by shaded arrows, and the pathway of electron transport from PSII via the plastoquinone pool (PQ) to photosystem I (PSI) is shown as an open arrow. Electrons can also enter the PQ pool by the PDS-mediated desaturation of phytoene. In the model, PDS transfers electrons from phytoene to the PQ pool and IMMUTANS acts after this step to reduce molecular oxygen. In the absence of IMMUTANS, electron flow from the PQ pool to PSI serves as the redundant function to generate green plastids. (This figure is from Wu et al., 1999).
