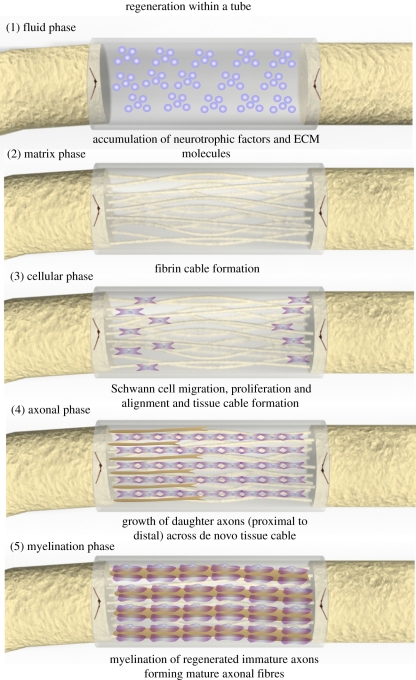
Figure 1.
Regenerative sequence occurring within a hollow NGC. Figure adapted from Belkas et al. [7]. This regenerative process occurs in five main phases: (1) the fluid phase: plasma exudate fills the conduit resulting in accumulation of neurotrophic factors and ECM molecules; (2) the matrix phase: an acellular fibrin cable forms between the proximal and distal nerve stumps; (3) the cellular phase: Schwann cells, endothelial cells and fibroblasts migrate (from the proximal and distal nerve stumps), align and proliferate along the fibrin cable forming a biological tissue cable; (4) axonal phase: re-growing axons use this biological tissue cable to reach their distal targets; (5) myelination phase: Schwann cells switch to a myelinating phenotype and associated with regenerated axons forming mature myelinated axons.