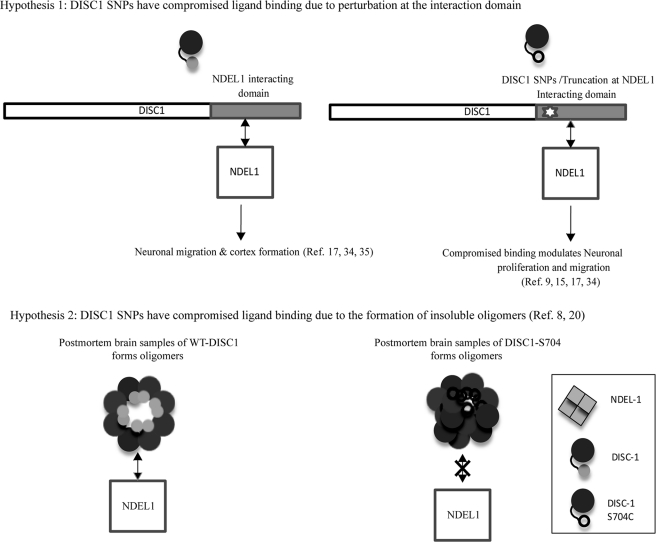
FIGURE 9.
Proposed mechanisms of DISC1-S704C-associated schizophrenia phenotype. a, hypothesis 1: schematic diagram of DISC1 primary sequence and its potential NDEL1 binding site (left). Schizophrenia risk DISC1 SNPs are located at the NDEL1 binding site, suggesting a probable perturbation at the DISC1-S704C-NDEL1 interactions (right). b, hypothesis 2: oligomerization condition of WT DISC1 extracted from the postmortem brain control sample (left) and DISC1-S704C (right) in the disease sample. Insoluble oligomerization condition of DISC1-S704C and a compromised NDEL1 binding were proposed due to the disease risk polymorphism.