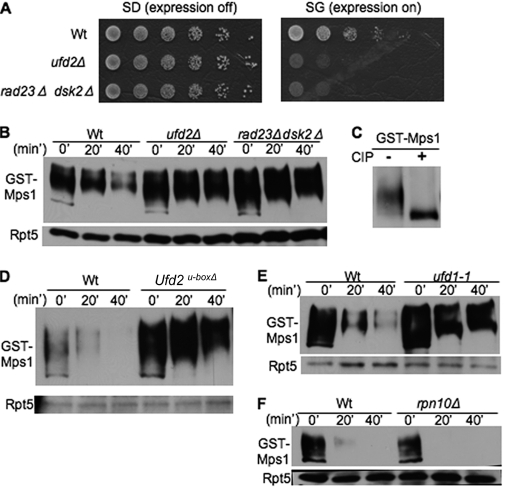
FIGURE 1.
Identification of Mps1 as substrate of Ufd2-Rad23/Dsk2 pathway. A, overexpression of Mps1 leads to slower growth of ufd2Δ or rad23Δ dsk2Δ double mutant cells. GST-His6-Mps1 isolated from the genome-wide screen was transformed into the wild type or the indicated mutants. These cells were grown to similar densities, and 5-fold serial dilutions were spotted onto SD or SG medium. B, efficient degradation of Mps1 requires Ufd2, Rad23, and Dsk2. Wild-type and ufd2Δ cells containing GAL1 promoter-driven GST-His6-Mps1 were first grown in raffinose-containing medium. Expression of Mps1 was induced by the addition of galactose. Samples were taken after promoter shut-off at the time points indicated and analyzed by anti-His6 Western blotting. Equal amounts of protein extracts were used and confirmed by blotting with anti-Rpt5 antibody in all of the expression shut-off experiments (lower panel). Proteins are identified on the left. C, Mps1 is phosphorylated. GST-His6-Mps1 was expressed in wild-type cells and recovered by immunoprecipitation. Mps1 immunoprecipitates were incubated with or without alkaline phosphatase and visualized by immunoblotting. CIP, calf intestinal phosphatase. D, the U-box motif is critical for Mps1 degradation. GST-tagged Mps1 was transformed into the wild type and ufd2U-boxΔ mutants. Mps1 degradation was assayed as described for B. E and F, Mps1 degradation requires Ufd1 but not Rpn10. GST-His6-Mps1 stabilities in ufd1-1 and rpn10Δ were determined.