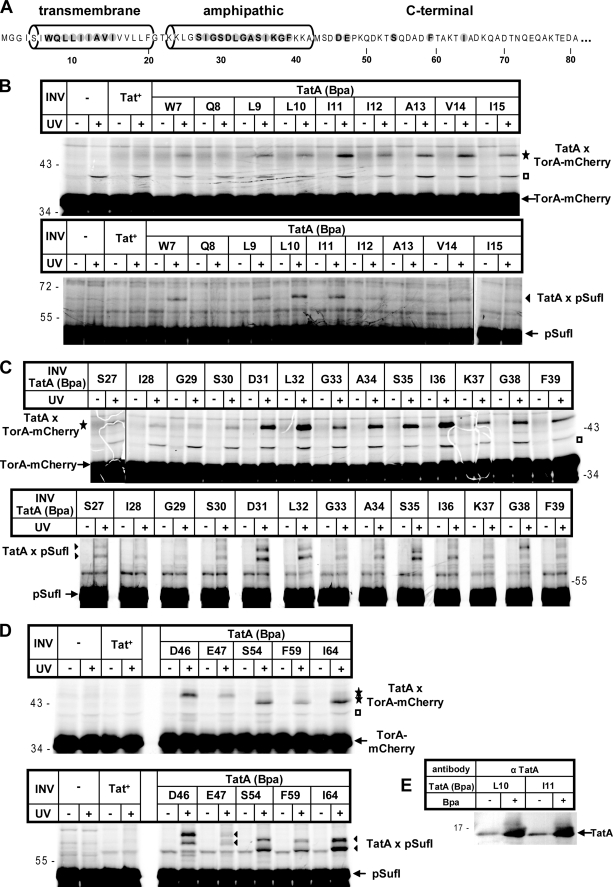
FIGURE 1.
Extensive contacts between large parts of TatA and membrane-bound RR precursor proteins. A, amino acid sequence of E. coli TatA (shown are 81 of the 89 residues) with its predicted transmembrane and amphipathic helices according to Ref. 16. Amino acids exchanged against Bpa by amber stop codon suppression are highlighted. B–D, the RR precursor proteins TorA-mCherry and pSufI were in vitro synthesized and radiolabeled by cell-free transcription/translation. Where indicated, E. coli INV were added 10 min after starting the synthesis. INV were prepared from TatABC-overproducing E. coli strains expressing either wild-type TatA (Tat+) or one of the indicated TatA (Bpa) variants. Following an incubation period of 25 min, reactions were stopped directly with TCA or first UV-irradiated on ice (+UV). Radiolabeled proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by phosphorimaging. UV-dependent adducts to TorA-mCherry and pSufI are labeled with stars and triangles, respectively. Open squares, TatA-independent cross-linking product. Numbers to the left and right indicate the molecular masses of marker proteins. E, INV prepared from strains that expressed the indicated TatA variants and that were grown in the absence or presence of Bpa were immunoblotted against anti-TatA antiserum (α TatA).