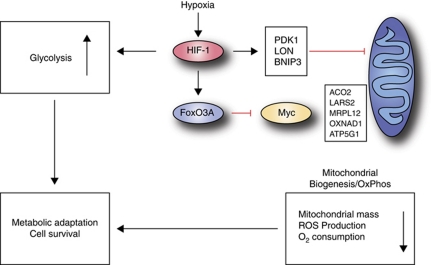
Figure 9.
Model. Hypoxia induces stabilization of HIF-1, which in turn leads to transcriptional regulation of its target genes. This leads to an increase in glycolytic flux through transcriptional upregulation of glucose transporters and glycolytic enzymes. In addition, HIF-1 transactivates target genes involved in inhibiting mitochondrial activity (PDK-1 and BNIP3) and adjusting oxygen consumption (LON protease) to hypoxic conditions. The hypoxic induction of FoxO3A leads to a direct and specific repression of a subset of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial genes that are Myc target genes. The combined effects of these adaptive measures serve to balance oxygen, ROS, and energy homeostasis in hypoxia, which is required for cell survival.