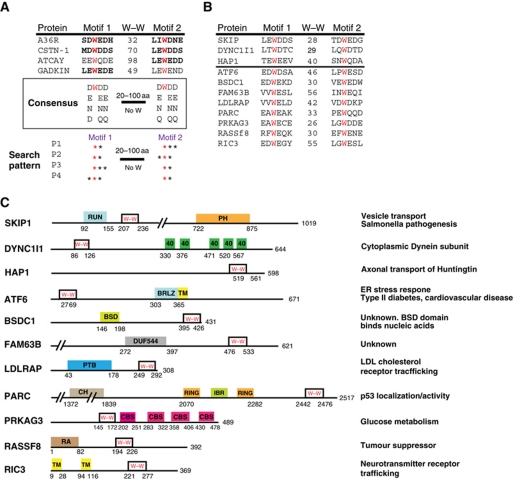
Figure 5.
Potential bipartite tryptophan KLC1/2-binding motifs are found in a wide range of proteins. (A) Sequence alignment showing the WD/E motifs in proteins previously shown to interact with KLC (bold text indicates experimental evidence). W–W indicates the number of residues separating the two tryptophans. A consensus based on these four proteins as well as conserved amino-acid substitutions is shown. A schematic representation of the set of patterns that was used to search the RefSeq database is shown. (B) Sequence alignment of bipartite tryptophan motifs in candidate KLC-binding proteins. SKIP, DYNC1I1 and HAP1 are known KLC-binding proteins. W–W indicates the number of residues between the two tryptophan residues highlighted in red. (C) Schematic representation of the location of bipartite tryptophan motifs in the proteins in (B) relative to other domains (from the Pfam database).