Figure 5.
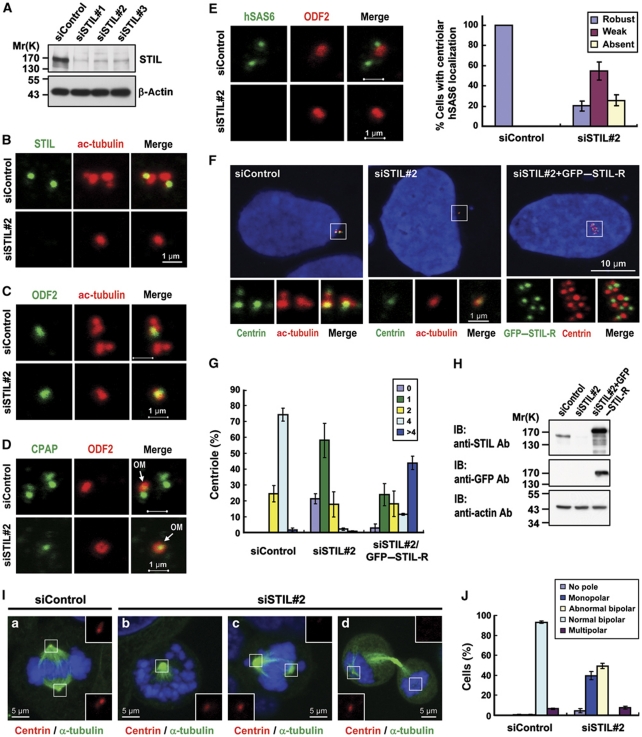
STIL depletion inhibits centriole duplication and siRNA rescue experiments. Because STIL is absent in G1 cells, we synchronized cells at G1/S by aphidicolin to ensure the detection of STIL after siSTIL treatment. U2OS cells were transfected with control siRNA (siControl) or STIL siRNAs (siSTIL-1, siSTIL-2, and siSTIL-3). Two days after transfection, the cells were treated with aphidicolin for another day and analysed by immunoblotting (A) or by immunofluorescence confocal microscopy using indicated antibodies (B–E). Depletion of STIL significantly inhibits hSAS6 targeting to the procentriole (E). A quantification of the centriolar signals of hSAS6 in siControl and siSTIL-treated cells is shown in (E) (right panel). Values are means of three experiments with s.d. bars (n=100 cells). In siRNA rescue experiments (F–H), U2OS cells were transfected with control siRNA (siControl) or siSTIL#2 for 16 h followed by siRNA-resistant GFP–STIL-R transfection for another 2 days. The cells were then processed for immunofluorescence confocal microscopy (F) or for immunoblotting (H). GFP–STIL-R was directly visualized by confocal fluorescent microscopy. To observe the mitotic effects generated by STIL depletion, U2OS cells were transfected with siControl (a) or siSTIL#2 (b–d). Three days after transfection, cells were analysed by immunofluorescence confocal microscopy using indicated antibodies (I). Histogram illustrating as percentages the numbers of centrioles (G, counted by centrin staining) and abnormal mitotic spindles (J) in siSTIL#2 treated cells. Error bars represent mean±s.d. of 100 cells from three independent experiments. OM, old mother centriole.