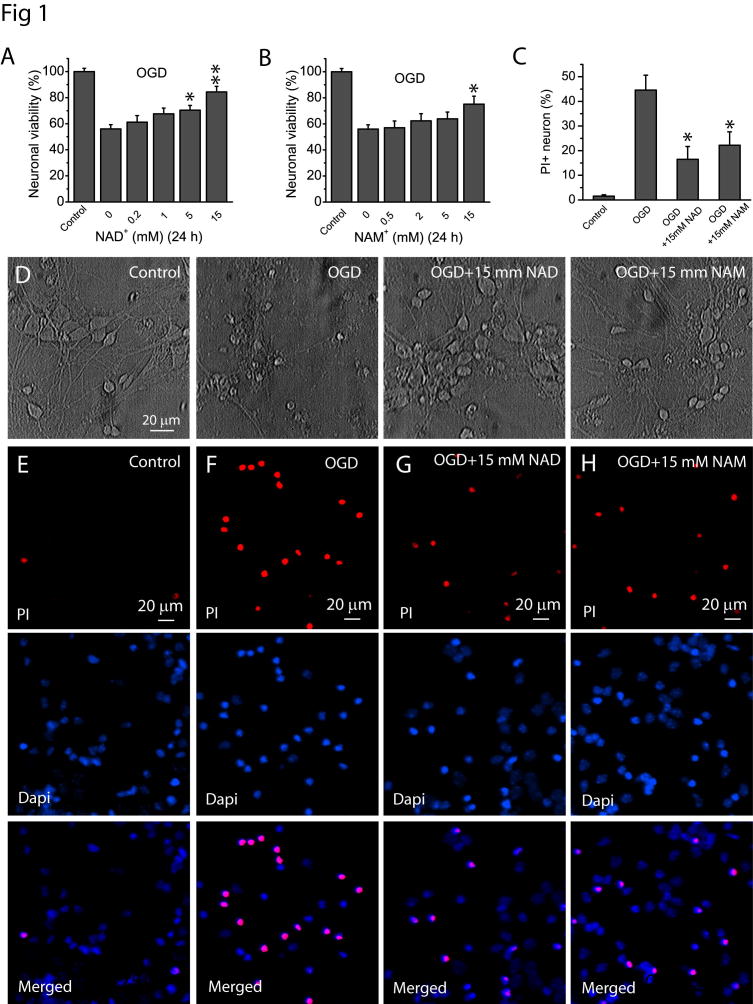
Fig 1. NAD+ and NAM protect neurons after OGD.
(A–B) Effect of NAD+ (A) and NAM (B) on neuronal viability after OGD. Neuronal cultures in 48 well plates were subject to OGD for 1.5 h in the absence and presence of NAD+ and NAM of various concentrations. NAD+ and NAM were continuously present after OGD for a total time of 24 h from the beginning of OGD. MTT assay was then performed to determine the effect of NAD+ and NAM on neuronal viability. (C) Summary of PI assay to confirm the neuronal protective effect of NAD+ and NAM after 1.5 h of OGD. The percentage of PI+ cells was calculated based on the total number of cells determined by Dapi-stained nuclei. Data from (A–C) were the mean value from 6 independent experiments, for each experiment, 3–4 parallel assays were performed and averaged as a single value for that experiment. *t-test with p<0.05; **t-test with p<0.005 vs no NAD+ or NAM treatment for (A–C). (D) Phase contrast image of cultured neurons at 24 h after 1.5 h of OGD in the presence and absence of 15 mM NAD+ and NAM. Notice the normal morphology of neurons treated with NAD+ and NAM. (E–G) Representative images of PI staining in the absence or presence of NAD+ and NAM. Neuronal cultures on glass coverslips in 48 well plates were subject to OGD for 1.5 h in the absence and presence of 15 mM NAD+ and NAM. NAD+ and NAM were continuously present after OGD for a total time of 24 h from the beginning of OGD. Neurons were then stained with PI and Dapi for 30 min for imaging and cell counting.