Figure 3. Systems biology in identifying miRNAs and their epigenetic modulation represents newer therapeutic strategies for pancreatic cancer.
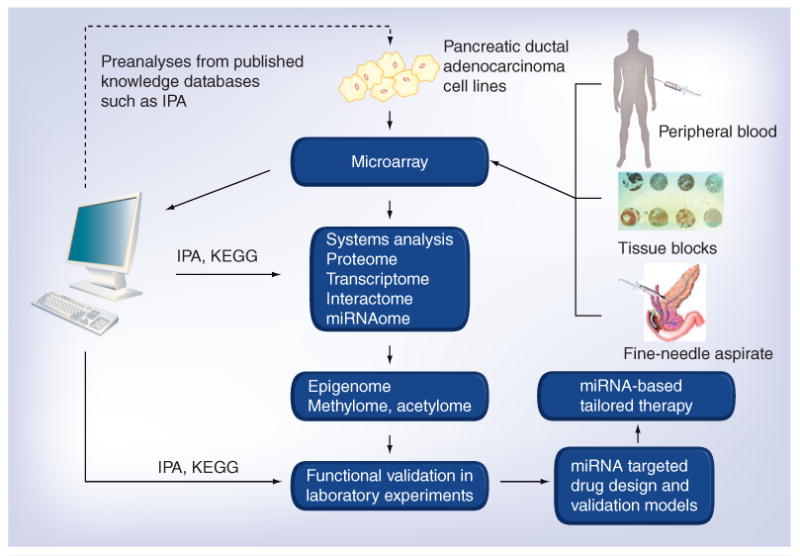
The flowchart describes the combined high-throughput experimental and computational approaches for the systems-level analysis of miRNA modulation and their targets. Preanalysis using published data can be performed computationally, followed by high-throughput (microarrays) experimental analyses on different samples from pancreatic cancer patients. The advantage of using such high-throughput technologies is also due to the fact that it requires a minimal amount of sample. Samples can be from peripheral blood during active disease or fine-needle aspirates that can be used to mine alterations in miRNAs. Additionally, the role of miRNAs and their epigenetic modulation on therapeutic response to different treatments can be evaluated in tissue block specimens obtained after chemotherapy or neoadjuvant therapies, and could be correlated with overall survival. Systems biology and network modeling could come into play as this technology can substantially reduce large microarray datasets into reduced, biologically meaningful and disease-specific information. Software such as IPA and KEGG can normalize microarray data and analyze it statistically to produce a preliminary list of gene, protein and miRNA changes with significantly up- or down-regulated expression. The technology could be beneficial for an in-depth understanding of the crosstalk within and across the proteome, transcriptome, interactome and even miRNAome because conventional molecular technology cannot produce such powerful information. The initial ‘omic information obtained from primary analysis can be utilized to investigate and analyze the epigenome, methylome and acetylome. Further validation analysis would be required to extract the biological information hidden behind the massive data. The raw and analyzed data are distributed within databases or web services, allowing other researchers to make use of this information. Finally, the obtained results can be tested using novel drug combinations using suitable test models to achieve a desirable clinical outcome for improving the overall survival of patients diagnosed with malignancies such as pancreatic cancer. IPA: Ingenuity Pathway Analysis; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
