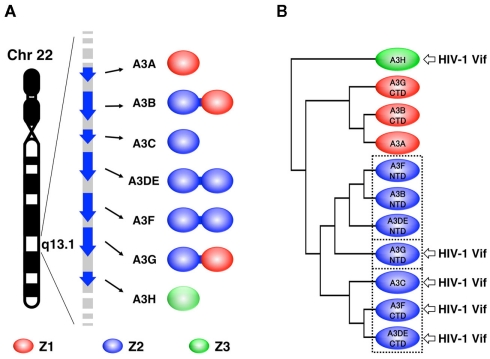
Figure 1.
Three types of Z domains in human A3 family. (A) Seven members of human A3 family, encoded by human chromosome 22, are illustrated. The protein products consist of one or two Z domains, each of which is phylogenetically grouped into three distinct types: Z1, Z2, and Z3. (B) Three subgroups of the Z2 domains are enclosed with dotted lines in the phylogenetic tree. The arrows point to the domains that are responsible for HIV-1 Vif interaction.