Figure 1.
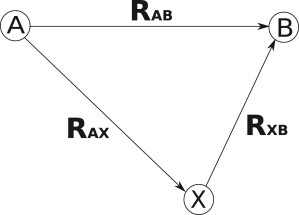
Definition of fractional RMS (fRMS). The fRMS is the metric used to assess how well normal modes describe the change from conformation A to B. When the modes are applied to A, they give the conformation X. The distance, in RMS space, between X and B is |RXB|, which is then normalized by the original distance between A and B, |RAB|, to give . If the normal modes describe the conformational change perfectly, conformation X will equal conformation B, and the fRMS value will be 0. The dot product, which is commonly used to assess normal mode performance, is the cosine of the angle BXA. It can be calculated as . If the angle AXB is a right angle, then .
