Figure 2.
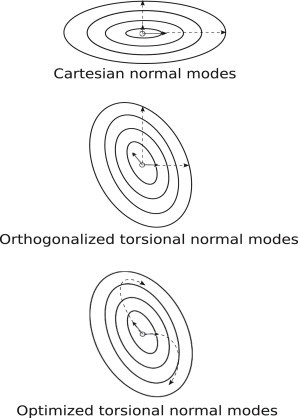
Energy surfaces and normal-mode projections. In this simple illustration, the energy surfaces and normal modes are shown projected into two-dimensional Cartesian space. The elliptical contour lines represent the energy surfaces, the solid arrows the normal mode displacement vectors, and the dashed lines the normal mode movement. Whereas displacement vectors at the origin are always straight lines in Cartesian space, movement along the torsion angle modes follows curved lines in Cartesian space. The displacement vectors at the origin are orthogonal in Cartesian modes but not in torsion-angle modes. The change of conformation between state A and state B is the optimal combination of movements along the dashed lines. This optimum is easily found when the lines are straight in Cartesian space but requires nonlinear optimization when the lines are curved.
