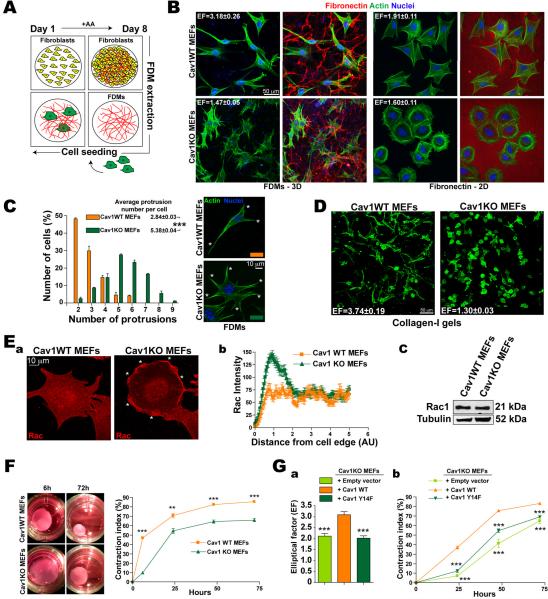
Figure 1. Cav1 regulated contractility controls matrix-induced cell morphology and reciprocal interaction with the 3D microenvironment.
(A) FDMs were generated from NIH-3T3 cells cultured with daily ascorbic acid (AA) supplement. (B) Cav1WT and KO MEFs were plated (4h) on NIH-3T3 FDMs (3D) or FN (5μg/ml, 2D) and labeled as indicated. Elliptical factors (EF) were calculated. (C) Quantification of protrusions per cell (means indicated). Representative Cav1WT and Cav1KO cells (asterisks mark protrusions). (D) Cav1WT and KO MEFs were embedded (6h) in Col-I gels (1mg/ml). EFs are indicated. (E) Rac1 distribution in Cav1WT and KO MEFs. (a) Rac1 immunostaining in cells plated (4h) on FN. Asterisks mark Rac1 foci. (b) Rac1 pixel intensity from the cell edge to the nucleus (c) Immunoblot showing total Rac1 expression. (F) Gel contraction by Cav1WT and KO MEFs embedded in Col-I gels. (G) Cav1-dependent cell elongation (a) and gel contraction (b) require Cav1-Tyr14.