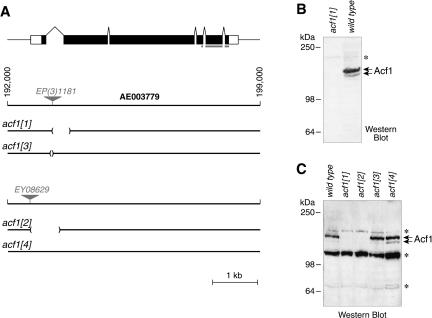
Figure 1.
Generation of null alleles of the acf1 gene. (A) The Drosophila acf1 gene. The structure of the acf1 gene and the location of the transposon insertions in EP(3)1181 and EY08629 are shown. The acf11 allele was generated by imprecise excision of acf1EP(3)1181, in which 499 bp of the first intron and second exon has been replaced by an 11-bp sequence from the P-element. The allele acf13 was generated by imprecise excision of acfEP(3)1181, in which 83 bp entirely within the first intron have been replaced by a 15-bp sequence from the P-element. The acf12 allele, in which 871 bp of the acf1 promoter and 5′ transcribed region is deleted, was generated by imprecise excision of acf1EY08629. The acf14 allele was generated by precise excision of acf1EY08629. AE003779 refers to the contig number of the Drosophila genome project (Adams et al. 2000). The noncoding and coding regions of the acf1 transcript are depicted as open and filled boxes, respectively. The gray bar indicates the Acf1 polypeptide that was used to prepare anti-Acf1 polyclonal antibodies. (B) Western blot analysis reveals that acf11 is a null allele. Nuclear extracts derived from 0- to 12-h embryos of homozygous acf11 flies or wild-type (Canton S) flies were subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-Acf1 antibodies. (C) Western analysis of Acf1 expression in embryos of acf1 alleles. Crude lysates of 0- to 12-h embryos (Ito et al. 1999) of homozygous wild-type, acf11, acf12, acf13, and acf14 flies were subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-Acf1 antibodies. Acf1 is not expressed in acf11 or acf12 embryos, but its expression is not significantly affected in acf13 or acf14 embryos. Asterisks indicate nonspecific bands.