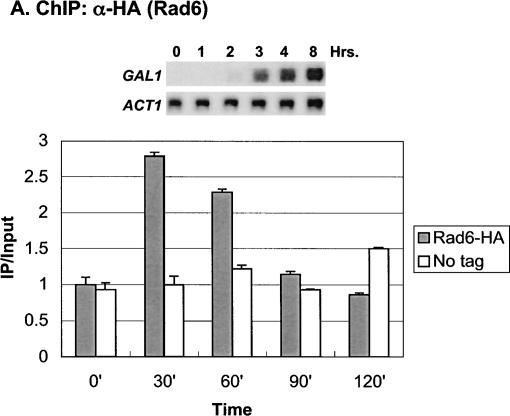
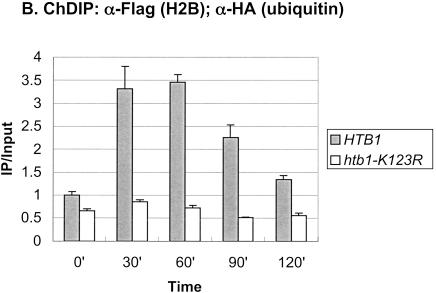
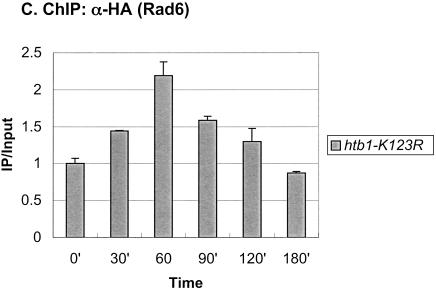
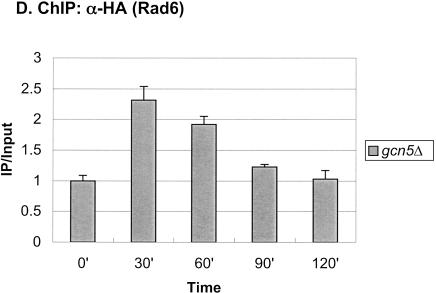
Figure 1.
Rad6 is transiently associated with the GAL1 promoter. (A) Strains YKH010 (Rad6-HA HTB1) and JR5-2A (No tag control HTB1) were grown in YPD medium and shifted to YP + 2% galactose medium, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) was performed with anti-HA antibodies at the indicated times. PCR analysis in real time was used to measure the abundance of GAL1 UAS sequences in immunoprecipitated (IP) DNA relative to input DNA. The Northern blot inset is from Figure 7A. (B) Strains YKH045 (Flag-HTB1; HA-ubiquitin) and YKH046 (Flag-htb1-K123; HA-ubiquitin) were grown as described in panel A. Chromatin double immunoprecipitation (ChDIP) was sequentially performed with anti-Flag and anti-HA antibodies, and PCR in real time was used to measure the abundance of GAL1 core promoter sequences in the IP DNA (α-HA) relative to input DNA (α-Flag). The data were normalized to the IP/Input ratios for INT-V, which is not regulated by galactose and thus served as a control. (C,D) Strains YKH017 (Rad6-HA htb1-K123R) and YCH001 (Rad6-HA HTB1 gcn5Δ) were grown as described in panel A, and ChIP was performed with anti-HA antibodies, followed by PCR analysis in real time using primers that detect the GAL1 UAS sequences.