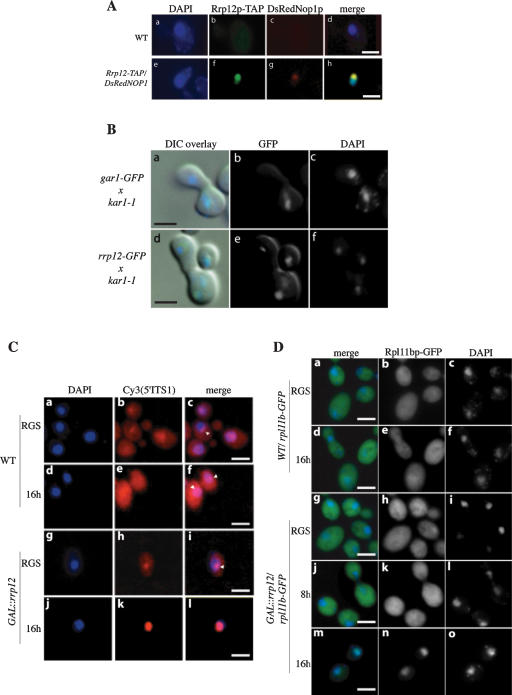
Figure 6.
Rrp12p is a nucleolar-cytoplasmic shuttling protein and required for export of both 40S and 60S subunits. (A) Rrp12p is predominately nucleolar. The GAL::rrp12–TAP strain also expressing the nucleolar marker DsRedNop1p (g) was examined by immunofluorescence using an anti-protein A antibody coupled to FITC (f). Also shown is the position of the nucleus visualized by DAPI staining (e), and a wild-type control strain (a–d). (B) Rrp12p can shuttle to an introduced nucleus in a heterokaryon. GAR1–GFP and RRP12–GFP cells were pregrown in YPD, treated with cycloheximide, and mated to kar1-1 cells (MS740). After zygotes were formed (∼1 h), the localization of GFP as well as DAPI staining of the nuclei was determined for Gar1p–GFP (b,c) and Rrp12p–GFP (e,f). Images have been oriented with the receptor nucleus at the top. Signals were merged with differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy images (a and d, respectively). (C) 40S export assay. FISH localization of the Cy3-labled 5′ITS1 probe, which detects the 35S and 20S pre-rRNAs. DAPI staining is shown in a, d, g, and j. The 5′ITS1 localization is shown in b, e, h, and k. Strains were grown in permissive RGS medium and transferred to glucose medium for 16 h. Nucleoli are indicated with arrows. (D) 60S export assay. Wild-type or GAL::rrp12 cells expressing Rpl11b–GFP from a CEN plasmid were grown in permissive RGS-containing medium and transferred to glucose-containing medium for 8 or 16 h. (c,f,i,l,o) DAPI staining of the nucleoplasm. (b,e,h,k,n) Rpl11b–GFP visualized by fluorescence microscopy.