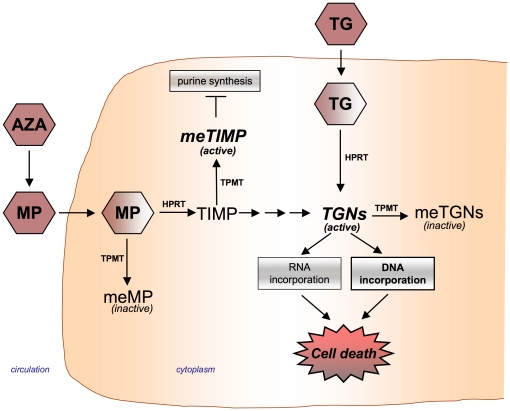
Figure 1. Thiopurine drug metabolism pathway.
Azathioprine (AZA) is a prodrug of mercaptopurine (MP). Thioguanine (TG) and MP can be converted by hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase (HPRT) to thioguanine nucleotide (TGNs) metabolites. MP can also be converted to the methylthioinosine monophosphate (meTIMP) by thiopurine methyltransferase (Tpmt) which inhibits purine synthesis; however, thioguanine bypasses the conversion to this metabolite. Thiopurines can be converted to inactive metabolites [i.e. methyl-mercaptopurine (meMP); methyl-thioguanine (meTG); and methyl-thioguanine nucleotides (meTGNs)] by Tpmt. TGN metabolites are incorporated into DNA and RNA leading to cell death. However, DNA incorporation is believed to be the primary mode of cytotoxicty.