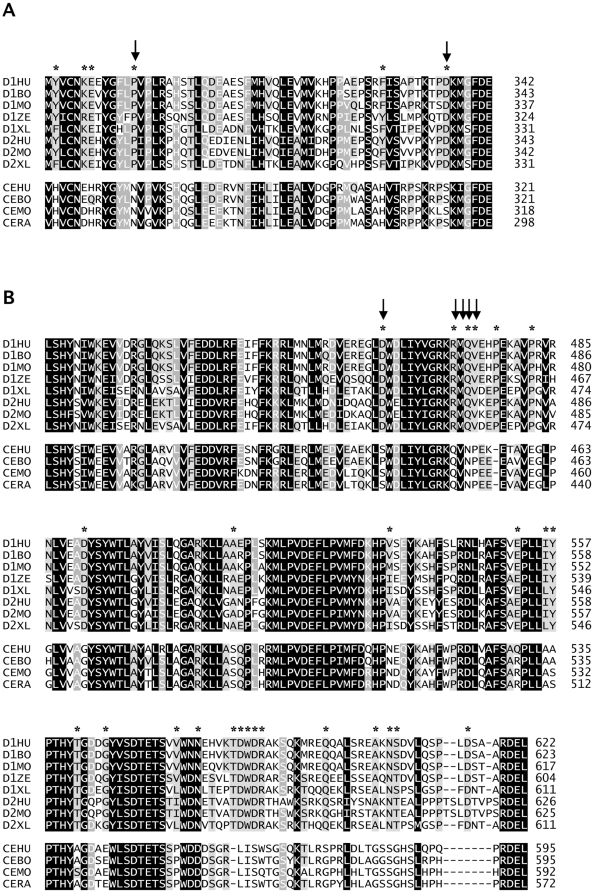
Figure 4. Multiple alignments of GLT25D1, GLT25D2 and CEECAM1.
A) The portion of the central domain essential for ColGalT activity is represented encompassing GLT25D1 amino acids 280 to 342. Sequences of GLT25D1 human (D1HU; Swiss-Prot:Q8NBJ5), bovine (D1BO; Swiss-Prot:A5PK45), mouse (D1MO; Swiss-Prot:Q8K297), zebrafish (D1ZE; Swiss-Prot:A5PMF6), xenopus (D1XL; Swiss-Prot:A0JPH3) ; GLT25D2 human (D2HU; Swiss-Prot:Q81IYK4), mouse (D2MO; Swiss-Prot:Q6NVG7), xenopus (D2XL; Swiss-Prot:Q5U483); CEECAM1 human (CEHU; Swiss-Prot:Q5T4B2), bovine (CEBO; Swiss-Prot:A7MB73), mouse (CEMO; Swiss-Prot:A3KGW5), rat (CERA; Swiss-Prot:Q5U309) were aligned using ClustalW. Black squares represent amino acids identical or strongly similar in all proteins, dark grey squares represent amino acids identical or similar in at least 10 proteins, light grey squares represent amino acids identical or similar in at least 7 proteins. The amino acids conserved in GLT25D1 and GLT25D2 but not in CEECAM1 are marked with a star at the top of the alignment. The residues P292 and D336 are marked with arrows. B) The alignment shows the portion of the C-terminal domain essential for ColGalT activity corresponding to GLT25D1 amino acids 414 to 622. The origin of the sequences and the markings are the same as in A.