Figure 3.
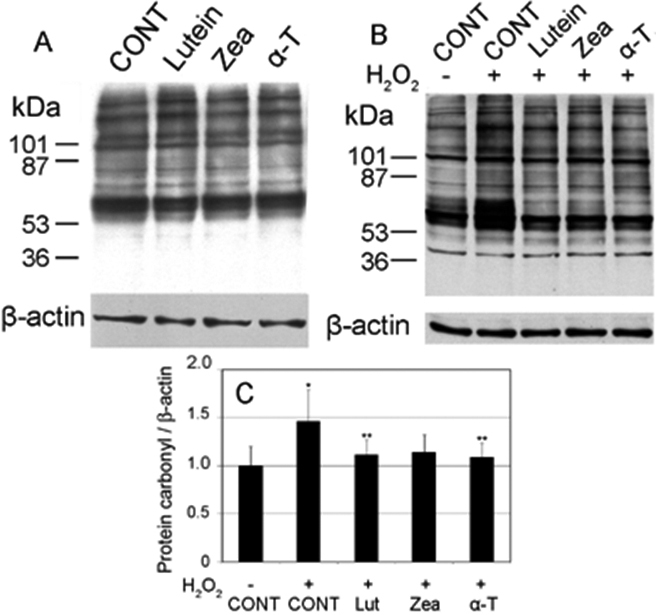
Supplementation with lutein, zeaxanthin, or α-tocopherol prevented H2O2-induced increase in levels of protein carbonyls in human lens epithelial cells (HLEC). Subconfluent HLEC were pre-incubated with or without 5 µM lutein, zeaxanthin, or α-tocopherol for 48 h and then exposed to 100 µM H2O2 for 1 h. Levels of protein carbonyls were determined by western blotting after derivatization with DNPH. β-Actin was used as the loading control. A: Effects of lutein, zeaxanthin, and α-tocopherol supplementation on levels of protein carbonyls in cells that were not exposed to H2O2. B: Effects of lutein, zeaxanthin, and α-tocopherol supplementation on levels of protein carbonyls in cells that were exposed to 100 µM H2O2, for 1 h. C: Densitometry quantification of western-blotting results in B (n=3). *Indicates a p<0.05 when comparing H2O2-exposed groups to the control group that were not treated with H2O2 and **indicates a p<0.05 when comparing lutein, zeaxanthin or α-tocopherol supplemented groups to the unsupplemented group upon exposure to 100 µM H2O2 for 1h.
