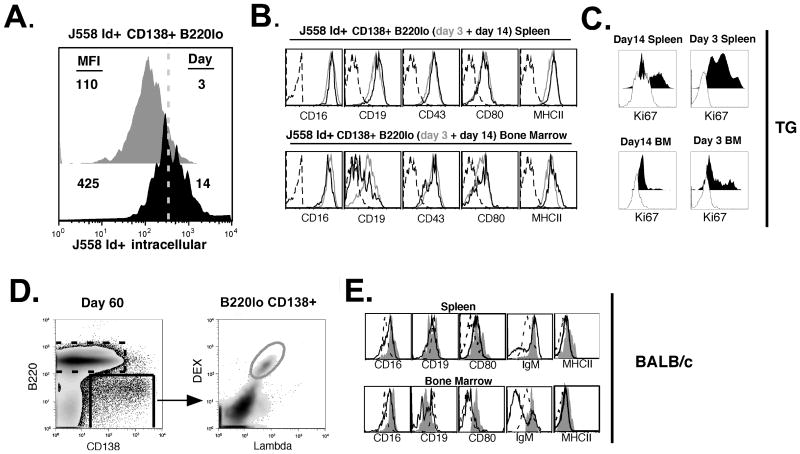
Figure 2. Mature DEX-specific plasma cells in VHJ558.3 TG and BALB/c mice maintain a plasmablast phenotype.
(A) Comparison of DEX-specific CD138+ B cells isolated from TG mice shows that larger amounts of intracellular DEX-specific IgM are found at 14 days (black histogram) after E. cloacae strain MK7 immunization than at 3 days (grey histogram). (B) Cell surface phenotypes of DEX-specific CD138+ cells detected with antibodies specific for CD16, CD19, CD43, CD80, and MHCII at 3 days (grey histogram) and 14 days (black histogram) after immunization, compared to an isotype matched control (dashed black histogram). (C) Ki67 expression by DEX-specific CD138+ cells 14 days and 3 days after immunization in the spleen (top panel) and the bone marrow (lower panel). Dashed histogram is that of the negative control sample. (D) Gating strategy to analyze DEX-specific λ+ CD138+ B cells generated in the spleen and bone marrow of BALB/c mice in response to E. cloacae strain MK7 immunization. (E) Phenotypes of B220 lo CD138+ λ+ DEX-binding B cells (solid grey histogram) at 60 days post immunization of BALB/c mice compared to bulk B220lo CD138+ B cells (dashed black histogram), and bulk B220+ CD138- B cells (black histogram). Data shown is representative of 5 VHJ558.3 TG and 5 BALB/c mice.