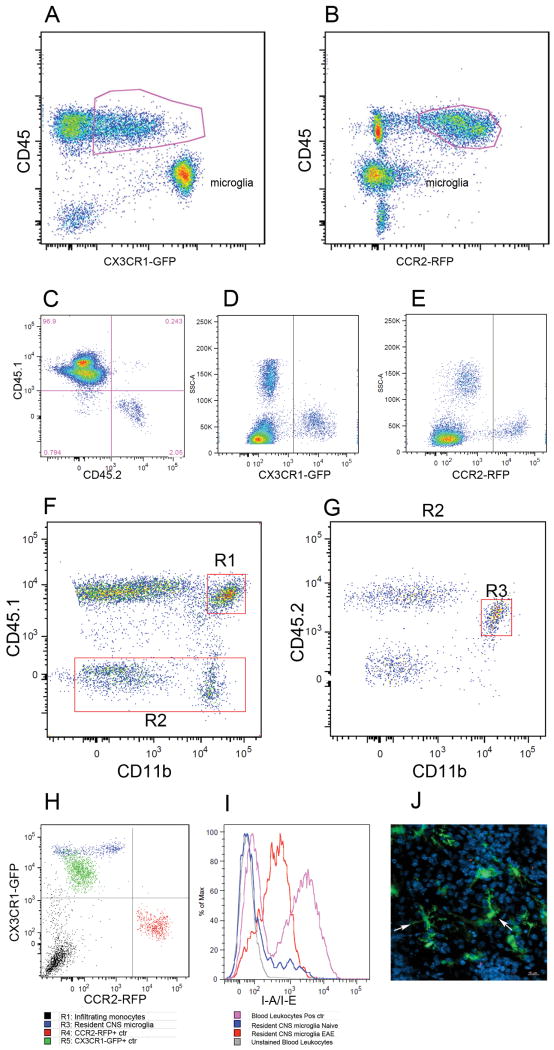
FIGURE 6. Analyses of monocyte subsets in brain lesions of EAE CX3CR1+/GFP CCR2+/RFP mice at peak disease.
Flow cytometry analysis of mononuclear cells isolated from adult brain at peak EAE disease shows that the CD45lo population contains CX3CR1bright microglial cells (A), contrasting their lack of CCR2-RFP expression (B). Degree of bone marrow recosntitution was evaluated by staining PBMCs with CD45.1 and CD45.2 antibodies (C). CX3CR1-GFP (D) and CCR2-RFP (E) positive controls were obtained from Cx3cr1GFP/+/CCR2+/+ or Cx3cr1+/+/CCR2RFP/+ mice respectively. Brain leukocytes were analyzed for CD45.1 and CD11b expression (F) and peripherally derived myeloid cell (R1) were distinguished from resident CD45.2+ CD11b+ cells via expression of the congenic markers (G, R3). Analyses of CX3CR1 and CCR2 based on activation of the transcription unit and expression of the GFP and RFP reporters (H) shows that resident microglial cells appear as CX3CR1-single positive. (I) activated resident cells up regulated MHC-II expression upon EAE induction as compared with naïve brains, and confocal imaging from diseased mouse brains shows morphologically activated microglia as CX3CR1-GFP bright cells (J). Results show one representative set of data from one mouse out of 8 analyzed by flow cytometry and histology.