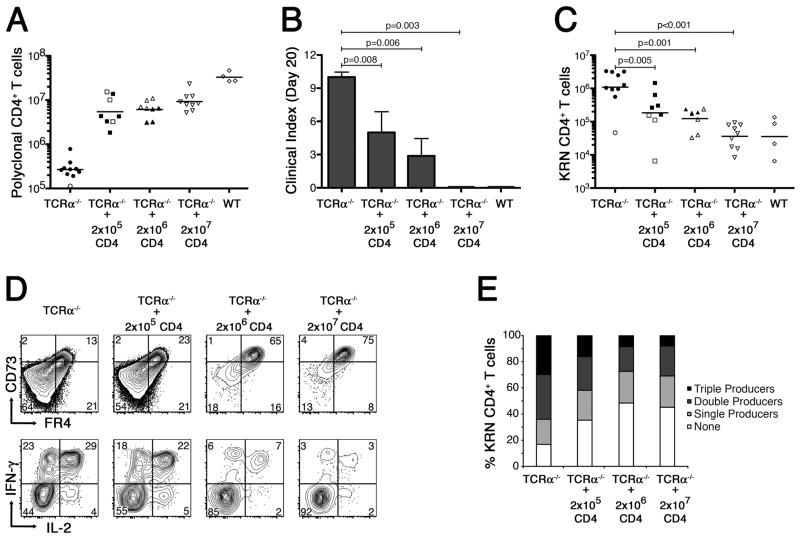
Figure 4.
Partial reconstitution of TCRα−/− B6×B6.g7 mice with polyclonal Foxp3+ CD4+ T cells prevents autoimmune arthritis by inducing clonal anergy in the GPI-reactive CD4+ T cells. A, Polyclonal CD4+ T cell counts in TCRα−/− B6×B6.g7 mice on day 20 after partial reconstitution, as indicated. Counts from tolerant WT B6.B6.g7 mice are also shown for comparison. B, Mean clinical score in each experimental group ±SEM. P values are based on the Mann-Whitney U test. C, Absolute number of KRN CD4+ T cells recovered from host animals following partial polyclonal CD4+ T cell reconstitution, as in panel A. D, In a separate experiment, FR4− and CD73− levels (top) were measured on KRN CD4+ T cells recovered from partially reconstituted TCRα−/− B6×B6.g7 mice (as indicated) 10 d after the KRN adoptive transfer. Flow cytometric measurement of IFNγ and IL-2 intracellular accumulation was also performed (bottom) on ex vivo PMA plus ionomycin stimulated KRN CD4+ T cells. E, Percentage of KRN CD4+ T cells recovered from various hosts (as in panel D) capable of synthesizing IL-2, IFNγ, and/or TNFα in various combinations. In panels A and C, filled symbols represent animals developing at least one arthritic joint; open symbols are animals that remained free of disease. Bars indicate the mean cell count, and P values are as indicated, using Student’s t test.