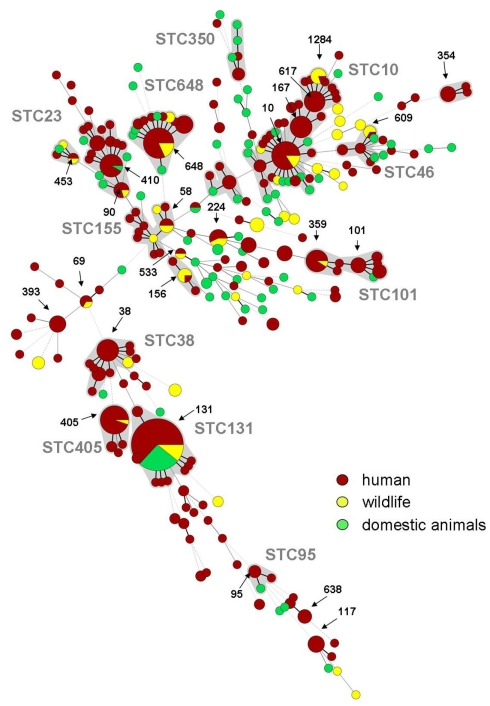
Figure 1.
Minimum spanning tree (MSTree) of human, domestic animals, and wildlife sequence types known for the production of ESBLs based on data of the MLST database (http://mlst.ucc.ie/mlst/dbs/Ecoli; n = 288 isolates identifiable as ESBLs, October 2011), previously published articles with human clinical background (Minarini et al., 2007; Yumuk et al., 2008; Blanco et al., 2009; Hrabak et al., 2009; Naseer et al., 2009; Oteo et al., 2009; Suzuki et al., 2009; Valverde et al., 2009; Coelho et al., 2010; Cortes et al., 2010; Peirano et al., 2010; Smet et al., 2010a; Zong and Yu, 2010; Ben Slama et al., 2011; Djamdjian et al., 2011; Leverstein-Van Hall et al., 2011; Mshana et al., 2011; Van Der Bij et al., 2011; Woerther et al., 2011) and data on wildlife given in Table 1. Red: human isolates, Green: domestic animals, Yellow: wildlife, Gray underplayed: Sequence type complexes, calculated with Bionumerics 6.6 (Applied Maths, Belgium).