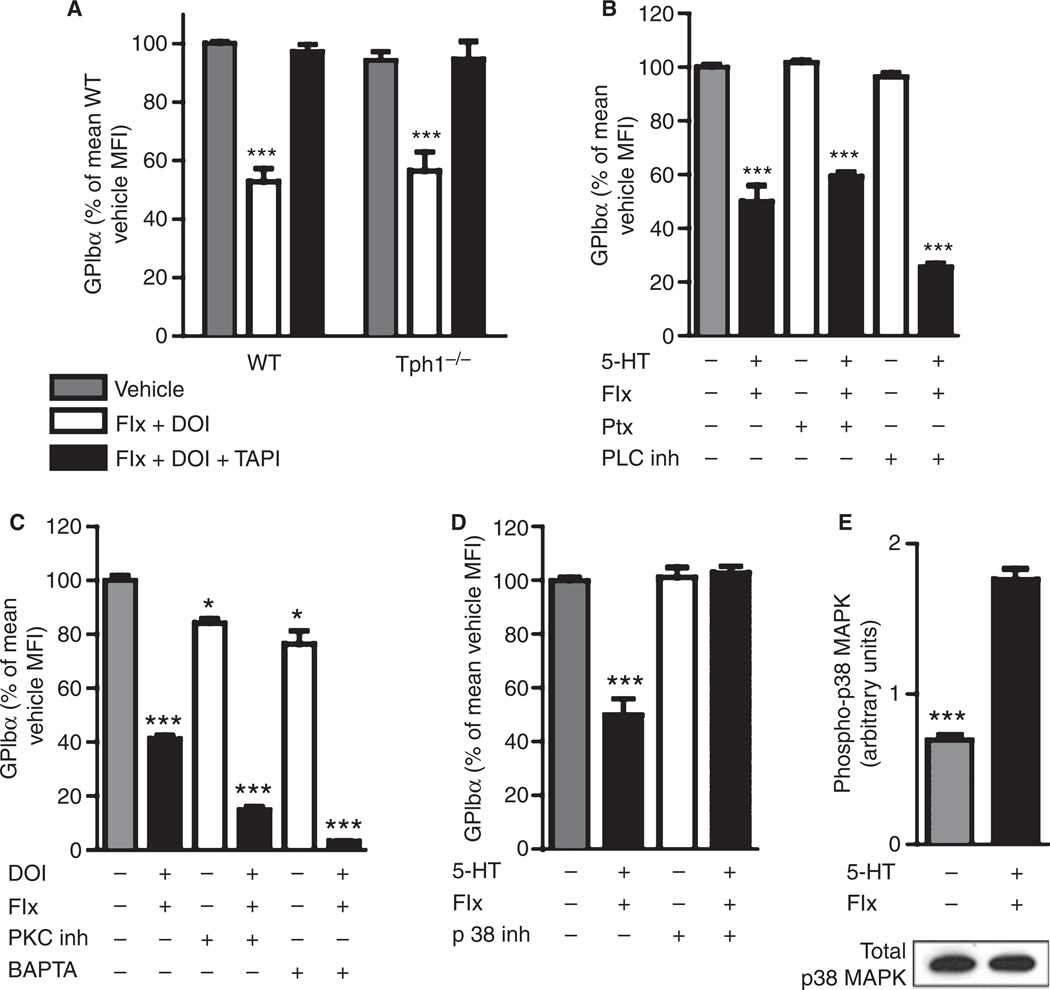
Fig. 3.
p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) mediates tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme activation after membrane 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor (5-HT2AR) stimulation. (A) Glycoprotein (GP)Ibα on isolated platelets after 20 µm fluoxetine (Flx), 50 µm (−)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine hydrochloride (DOI) and 5 µm tumor necrosis factor-alpha protease inhibitor (TAPI-1) incubation as indicated (n ≥ 6 mice). (B) Signal transduction by pertussis toxin (Ptx)-sensitiveG-proteins was inhibited by 10 µg mL−1 Ptx or the phospholipase C (PLC) inhibitor U73122 (10 µm, n = 4) in wild-type (WT) platelets. (C) Protein kinase C (PKC) was inhibited with 5 µg mL−1 Ro31-8220, and intracellular Ca2+ was chelated with 30 µm BAPTA (n = 4). (D) Signaling through p38 MAPK was inhibited by 20 µm SB203580 (n = 6). (E) Phosphorylation of p38 MAPK after 15 min of incubation with 20 µm fluoxetine and 100 µm 5-HT was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and p38MAPK protein in the same samples by western blot (representative blot, n = 3). *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 as compared with wild type/vehicle.