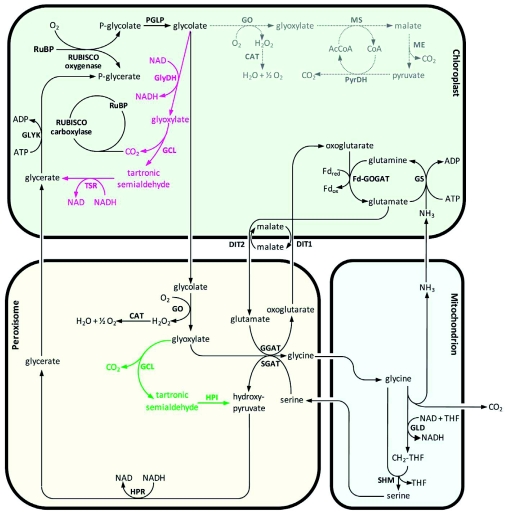
Figure 7.
Transgenic pathways for the reduction of photorespiratory losses in Arabidopsis.
Overview of the major photorespiratory pathway (black) and different transgenic approaches for the reduction of photorespiratory losses (red, dotted grey, and green). The red pathway shows the glycerate pathway from E. coli integrated into the chloroplast, the dotted grey pathway shows the alternative complete oxidation of glycolate inside the chloroplast, and the green pathway shows a shortcircuit inside the peroxisome. RuBP, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate; RUBISCO, RuBP carboxylase/oxygenase; PGLP, phosphoglycolate phosphatase; GO, glycolate oxidase; CAT, catalase; GGAT, glyoxylate:glutamate aminotransferase; SGAT, serine:glyoxylate aminotransferase; DIT1, dicarboxylate transporter 1; DIT2, dicarboxylate transporter 2; GLD, glycine decarboxylase; SHM, serine hydroxymethyltransferase; HPR, hydroxypyruvate reductase; GLYK, glycerate kinase; GS, glutamine synthetase; Fd-GOGAT, glutamine:oxoglutarate aminotransferase; GlyDH, glycolate dehydrogenase; GCL, glyoxylate carboligase; TSR, tartronic semialdehyde reductase; MS, malate synthase; ME, malic enzyme; PyrDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; AcCoA, acetylated Coenzyme A; CoA, Coenzyme A; HYI, hydroxypyruvate isomerase; THF, tetrahydrofolate; CH2-THF, methylene-THF. The stoichiometry of the reactions is not included.