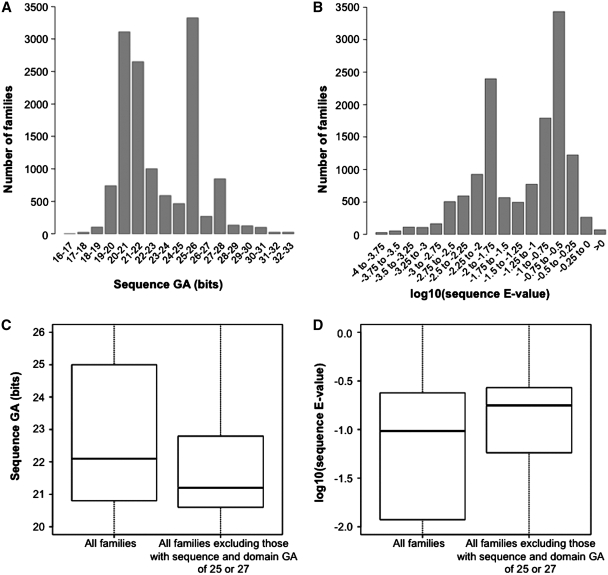
Figure 4.
Distribution of sequence gathering (GA) thresholds and of corresponding E-values. (A) Distribution of sequence GAs for all Pfam-A families. Note that intervals are such that, for example, ‘25–26’ translates into 25 ≤ sequence GA(bits) < 26. (B) Same as the histogram in panel (A), with log10(E-values) in place of GAs. E-values are calculated from GAs according to the following formula: E = N × exp[−λ·(x − τ)], where x is the bit score GA, λ and τ are parameters derived from the HMM model (λ is the slope parameter, τ is the location parameter) and N is the database size (in this case the size of UniProtKB) (22). (C) Box-plot of all Pfam families’ GAs (left side; median = 22.1, 25th percentile = 20.8, 75th percentile = 25.0), and for all families excluding those where both sequence and domain thresholds equal 25.0 or 27.0 (right side; median = 21.2, 25th percentile = 20.6, 75th percentile = 22.8). (D) Same as (C) with log10(E-values) in place of GAs. E-values calculated as in panel (B). Left side: median = 0.096, 25th percentile = 0.012, 75th percentile = 0.24. Right side: median = 0.18, 25th percentile = 0.057, 75th percentile = 0.27. Note that values reported here for median and percentiles are for E-values and not log10(E-values).