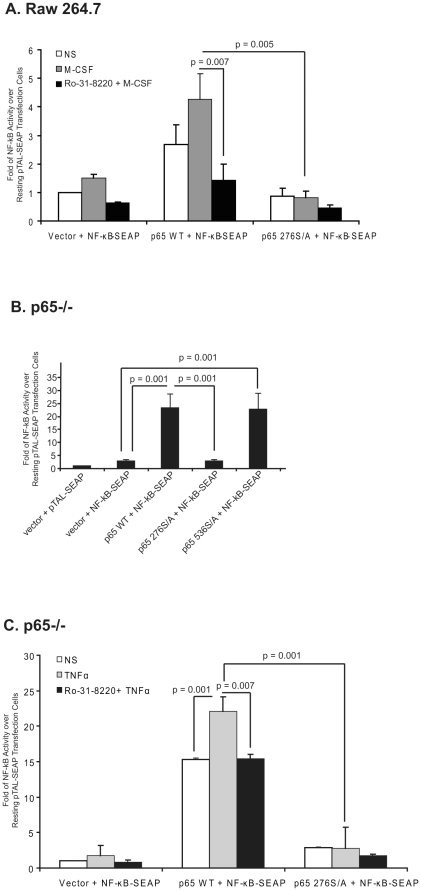
Figure 8. NF-κB p65 Ser276 is essential in regulating NF-κB activity.
(A) Raw 264.7 cell line was transiently transfected with pNF-κB-SEAP along with empty vector or plasmid encoding either NF-κB p65 WT or NF-κB p65 276S/A. The cells were transfected for 18-24 hours, serum starved for 4 hours, and then incubated with 10 µM of Ro-31-8220 for 30 minutes prior to treatment with 100 ng/ml of M-CSF for 2 hours and SEAP secretion in the medium was measured. (B) NF-κB p65−/− cell line was transiently transfected with pNF-κB-SEAP along with empty vector or plasmid encoding either NF-κB p65 WT, NF-κB p65 276S/A, or NF-κB p65 536S/A. The cells were cultured for 24 hours and then serum starved for 4 hours. Cells were then incubated in fresh DMEM medium for 2 hours and SEAP secretion in the medium was measured. The results shown are fold change over empty vector + pTAL-SEAP. (C) NF-κB p65−/− cell line was transiently transfected with pNF-κB-SEAP with either empty vector or plasmid encoding either NF-κB p65 WT or NF-κB p65 276S/A. The cells were transfected for 24 hours and serum starved for 4 hours, and then incubated with 10 µM of Ro-31-8220 for 30 minutes prior to treatment with 10 ng/ml of TNFα. The supernatant were collected after 2 hours of treatment and SEAP secretion in the medium was measured. The results shown are the fold change over empty vector + pNF-κB-SEAP. Data shown are mean ± S.E.M for at least three independent experiments performed in duplicate.