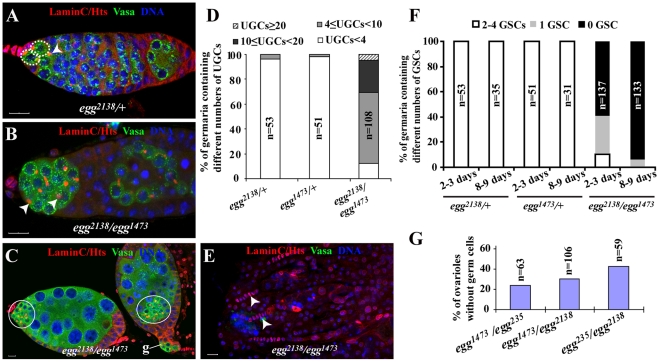
Figure 1. egg is required for GSC maintenance and germ cell differentiation.
Control and egg mutant germaria are labeled for Lamin C (red, terminal filament and cap cells), Hts (red, spectrosomes and fusomes), Vasa (green, germline cells) and DAPI (blue, nuclei). (A) A week-old egg heterozygous control germarium showing two GSCs (broken circles) and one CB (arrowhead). (B) 3-day-old mutant egg germarium shows the accumulation of spectrosome-containing undifferentiated germ cells (UGCs) (arrowheads), indicative of differentiation defects. (C) The egg mutant chambers following the germarium (indicated by g) contain both differentiated germ cells and a cluster of undifferentiated spectrosome-containing single germ cells (circled). (D) 3-day-old egg mutant germaria contain more UGCs than the heterozygous controls. Germaria are categorized based on the UGC number. “n” indicates the number of germaria examined for each genotype. (E) Week-old egg mutant germaria showing only remaining TFs (arrowheads) and complete absence of germ cells including GSCs, which is indicated by absence of Vasa expression. (F) GSCs are gradually lost in egg mutant germaria. Germaria are categorized by the number of GSCs per germarium. (G) Germless ovarioles in 3–5 day-old ovaries of different egg mutant combinations are consistently observed. Scale bars represent 10 µm.