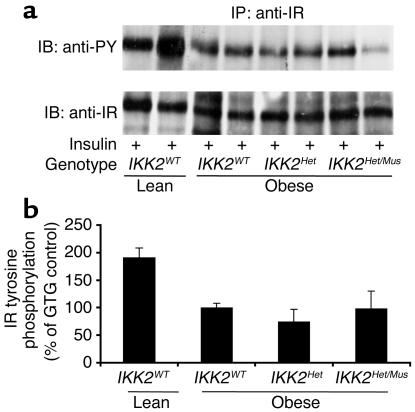
Figure 5.
Insulin-stimulated IR activation in skeletal muscle of IKK2-deficient mice. (a) Protein extracts isolated from skeletal muscle of mice, which had been injected with 5 IU of regular insulin 5 minutes before harvesting, were immunoprecipitated with an anti–IR-specific antiserum. The upper panel shows Western blot analysis using an anti–phosphotyrosine-specific antibody (anti-PY). The lower panel shows the autoradiogram after reprobing of the same blot with an anti-IR antiserum. IB, immunoblot; IP, immunoprecipitation. (b) Shown is the densitometric quantification of insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the IR β subunit from multiple experiments as outlined in a. The insulin-stimulated IR tyrosine phosphorylation of obese control (IKK2WT) mice was arbitrarily set as 100%. The results represent the mean of two to five animals of the indicated genotype. Insulin-stimulated IR tyrosine phosphorylation was significantly decreased in obese versus lean animals (P < 0.05), but without significant differences between obese animals of the different IKK2 genotypes.