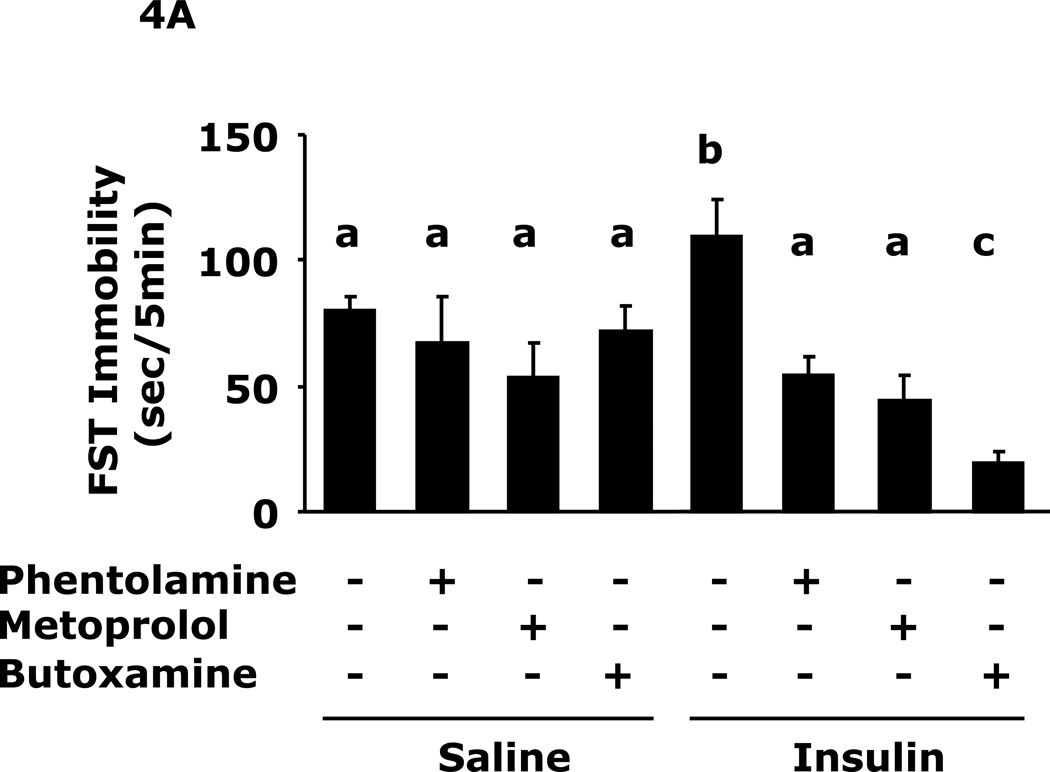
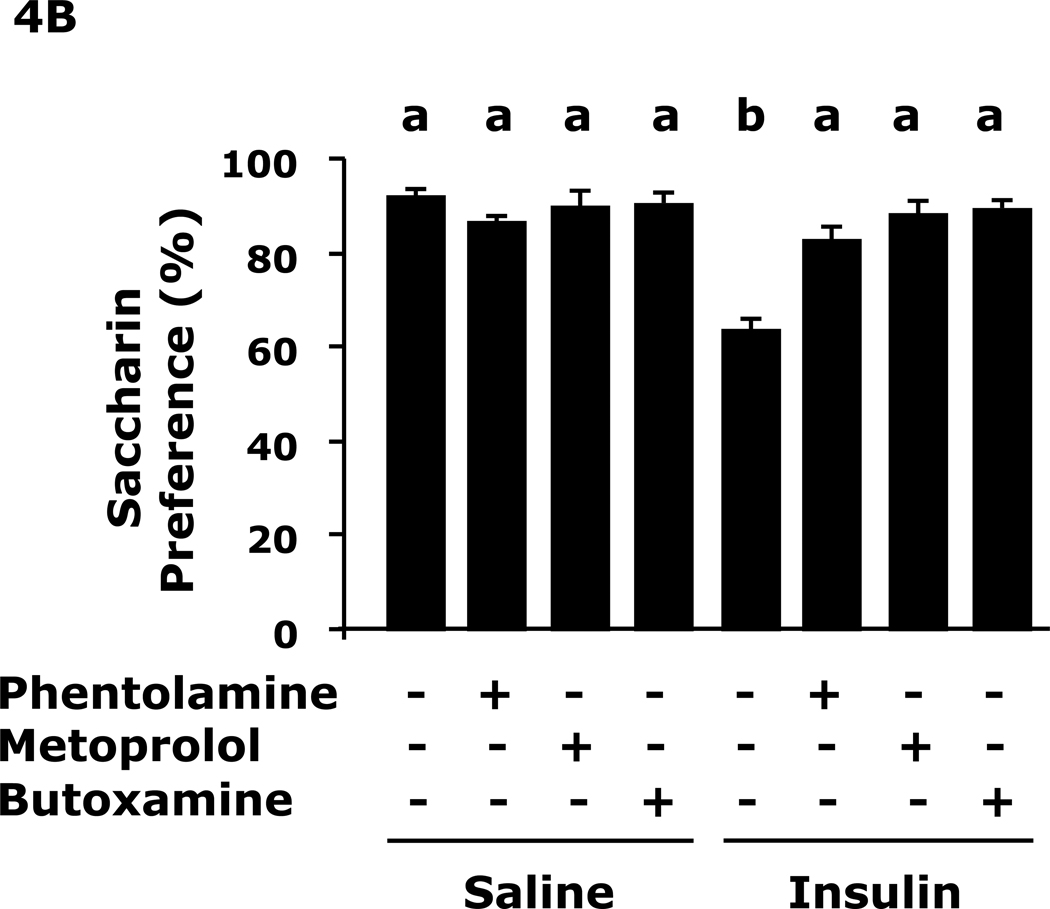
Fig. 4. Adrenergic antagonists block insulin-induced immobility and loss of saccharin preference.
A, After a 12 h fast mice were administered either saline or insulin IP. Immobility in the FST was measured at 24 h after saline or insulin injection in the presence or absence of the indicated adrenergic antagonists. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM; n=8/group. Two-way ANOVA revealed main effects of pretreatment (p<0.001) and pretreatment-treatment interaction (p=0.008). Bars without a common superscript letter are different (p<0.05). B, After a 12 h fast, mice were administered either saline or insulin IP. Saccharin preference was measured at 24 h after saline or insulin injection in the presence or absences of the indicated adrenergic antagonists. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM; n=8/group. Two-way ANOVA revealed main effects of pretreatment (p=0.0022), treatment (p<0.001) and pretreatment-treatment interaction (p<0.001). Bars without a common superscript letter are different (p<0.05).