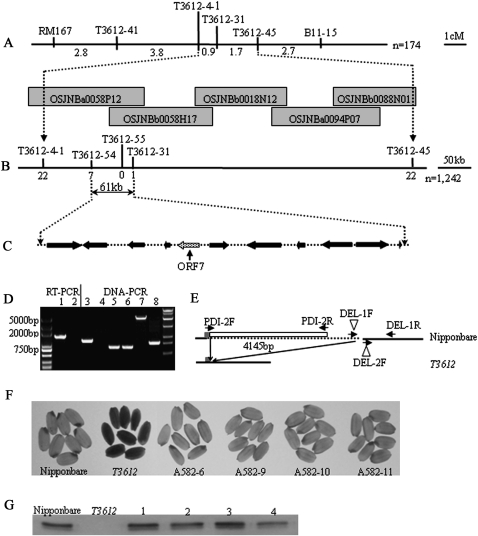
Fig. 3.
OsPDIL1-1 is the gene responsible for the T3612 mutant phenotype. (A) The mutated gene was mapped to the short arm of chromosome 11 between molecular markers T3612-4-1 and T3612-45. Genetic distances and names of the molecular markers are indicated (n =174). OSJNBa0058P12, OSJNBb0058H17, OSJNBb0018N12, OSJNBa0094P07, and OSJNBb0088N01 are BAC clones covering this locus. (B) The location of the mutation was narrowed to a 61 kb genomic region between T3612-54 and T3612-31. The number of recombinants is indicated below the molecular marker (n = 1242). (C) Gene prediction indicates 11 open reading frames in the critical region. The candidate gene (ORF7) is shown by an arrow. (D) PCRs based on cDNA (lanes 1,2) and genomic DNA (lanes 3–8) reveal the deletion in the T3612 PDIL1-1 allele. Lanes 1 and 2, PDI-2F/PDI-2R; lanes 3 and 4, DEL-1F/DEL-1R; lanes 5 and 6, DEL-2F/DEL-1R; lanes 7 and 8, PDI-2F/DEL-1R; lanes 1, 3, 5, and 7, cv. Nipponbare; lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8, T3612. (E) The deletion sequence (broken line) and primer annealing sites (indicated by arrows). The white box shows the deleted part of PDIL1-1. (F) Phenotypes of T1 kernels in four independent complemented lines. (G) PDIL1-1 protein was present in vitreous T1 grains. Lanes 1–4 represent four complementation lines shown in (F).