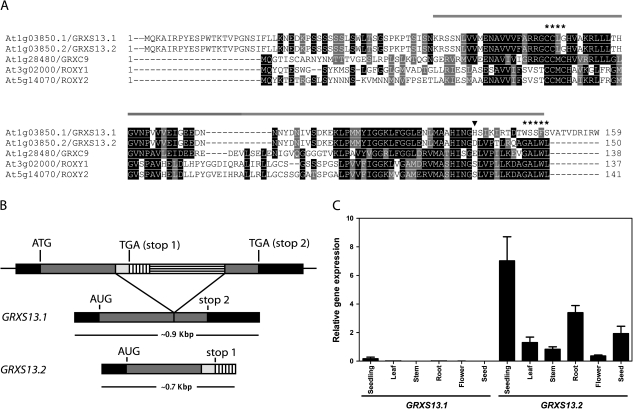
Fig. 1.
The GRXS13 gene codes for two CC-type GRX isoforms, GRXS13.2 being the predominantly expressed isoform in Arabidopsis seedlings. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of amino acid sequences for GRXS13 isoforms and the three previously characterized CC-type GRXs from Arabidopsis (GRXC9, ROXY1, and ROXY2). The glutaredoxin domain (amino acids 53–149; http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q84TF4) is indicated by the line drawn above the sequences; the CCLG active site and the GALWL motif are indicated by asterisks (*); GRXS13.1 and GRXS13.2 are identical up to residue 136 (arrowhead). Black boxes are used to indicate amino acid identity, while grey boxes indicate amino acid similarity. (B) Transcript processing of GRXS13 gene variants. The 23 amino acid C-terminus of GRXS13.1 is encoded by the second exon, while the 14 amino acid C-terminus of GRXS13.2 is encoded by part of the gene intron. (C) Expression pattern of GRXS13 gene variants in Arabidopsis seedlings (15 d old), in leaves, stems, roots, and flowers from adult plants (5 weeks old), and in seeds. GRXS13.1 and GRXS13.2 transcript levels were quantified by qRT-PCR and normalized by clathrin transcript levels. Data are presented as normalized transcript levels and correspond to mean values ±SD from three biological replicas.