Figure 2. ARF and ARL functions in the secretory pathway and in specialized transport.
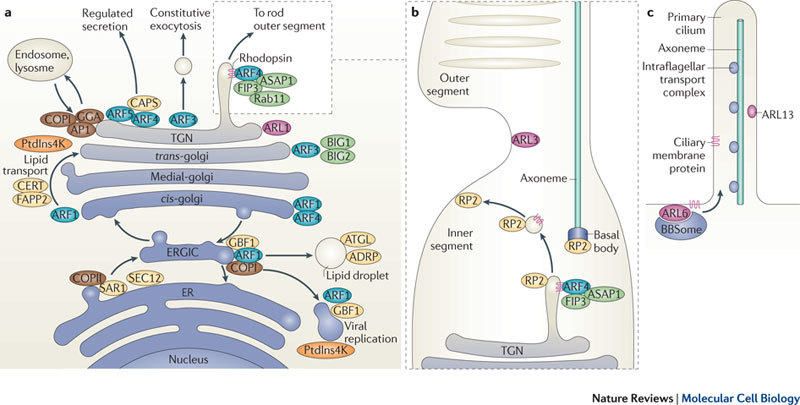
a | ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) proteins have distinct localizations and functions in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)–Golgi system. ARF1 and ARF4 localize to the early cis-Golgi and ARF3 specifically localizes to the trans-Golgi network (TGN). In addition to the recruitment of coat proteins (coatomer complex I (COPI), GGA (Golgi-localized, γ-ear-containing, ADP-ribosylation factor-binding protein) and adaptor protein 1 (AP1)) to the Golgi, ARF1 binds to ceramide transfer (CERT) and FAPP2 to mediate the transport of ceramide and glucosylceramide lipids from the cis-Golgi to the trans-Golgi. At the ER–Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC), ARF1 and its guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) GBF1 act with COPII to regulate the formation of lipid droplets and for the replication of several viruses. CAPS (Calcium-dependent activator protein for secretion), which is involved in regulated secretion, is recruited to the TGN by ARF4 and ARF5. At the ER, SAR1, activated by SEC12, recruits COPII to allow vesicle transport to the Golgi. b | In retinal cells, ARF4 binds specifically to rhodopsin in the TGN membrane and, together with FIP3, ASAP (ARF GAP containing SH3, ankyrin repeat and PH domains) and Rab11, it facilitates the transport of rhodopsin in transport vesicles from the inner segment to the outer segment, which is a specialized cilium. ARF-like 3 (ARL3) has been found to be localized to the connecting cilium, and retinitis pigmentosa 2 (RP2; also known as XRP2), an ARL3 GAP, localizes to the TGN, the basal body and the membrane adjacent to the connecting cilium. c | In primary cilia, ARL6 recruits the BBSome coat complex that facilitates the transport of membrane proteins into the cilium. ARL13 is localized to the cilium and has been implicated in intraflagellar transport. ADRP, adipose differentiation-related protein (also known as adipophilin); ATGL, adipose triglyceride lipase; PtdIns4K, phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase.
