Figure 3. The localization and function of ARF and ARL proteins in endosomal–lysosomal trafficking.
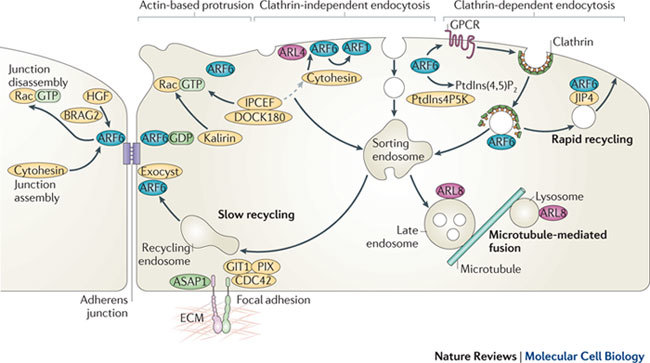
At the plasma membrane, ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6) activates phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase (PtdIns4P5K) to generate PtdIns-4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2) and, together with ARF-like 4 (ARL4), recruits cytohesin (also known as ARNO) guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) that can lead to further activation of ARF6 or ARF1. Cytohesins associate with the IPCEF (interactor protein for cytohesin exchange factors)–DOCK180 complex, which activates Rac, but another Rac GEF, Kalirin, can be recruited to membranes by ARF6•GDP. ARF6 at the plasma membrane can regulate the membrane lipid composition, alterations in cortical actin to drive protrusions (for example, during cell migration), and endocytosis of ligand-activated guanine-nucleotide-binding (G) protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) via clathrin-dependent endocytosis. ARF6 and the microtubule motor adaptor protein JNK-interacting protein 4 (JIP4) promote rapid recycling of endosomal membrane back to the cell surface, and ARF6, together with the exocyst complex, also affects slow recycling from sorting endosomes. ARF1 has been implicated in clathrin-independent endocytosis of glycosyl PtdIns (GPI)-anchored proteins in some cells. ARF6 and the ARF6 GEFs cytohesin and BRAG2 have been implicated in both assembly and disassembly of adherens junctions. Two ARF GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs), ASAP1 (ARF GAP containing SH3, ankyrin repeat and PH domains 1) and GIT1, localize to focal adhesions that mediate adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM), and GIT1 interacts with PIX, a GEF for CDC42. ARL8 is required for fusion of multivesicular late endosomes with lysosomes and is involved in transport along microtubules. HGF, hepatocyte growth factor.
