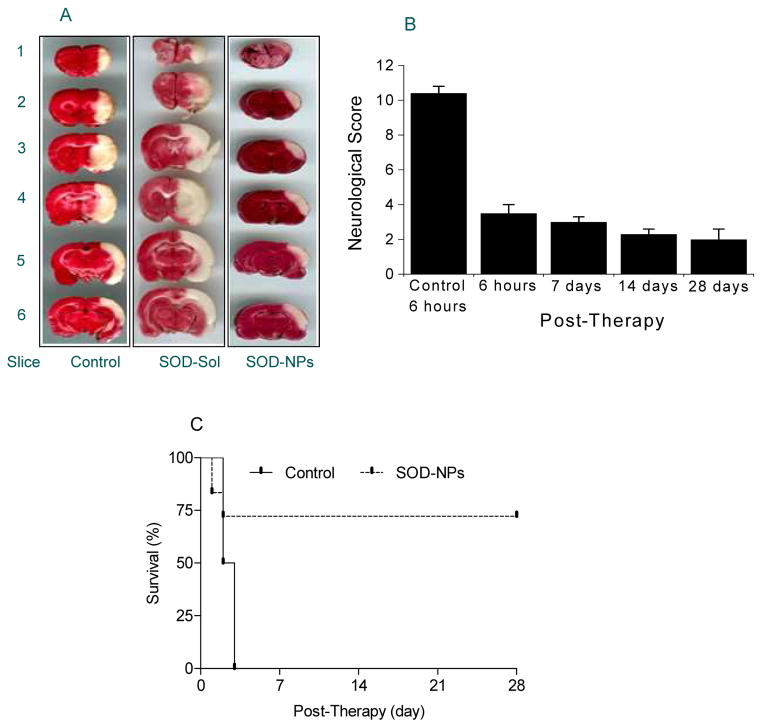
Figure 2.
Efficacy of SOD-NPs in rat stroke model. Transient focal cerebral ischemia was accomplished by middle cerebral artery occlusion using a suture in rats. One hour after ischemia, a suspension of SOD-NPs was infused through the carotid artery at the time of reperfusion. In acute studies, animals were evaluated for neurological parameters prior to euthanization at 6 hrs following reperfusion; brain were harvested to measure infract volume. In chronic studies, the same protocol was followed but animals were allowed to recover. Different controls were used including control NPs, SOD in solution, control NPs mixed with SOD in solution. SOD-NPs reduce infarcted area, improve neurological scores, and increase survival in rat middle cerebral artery occlusion ischemic stroke model. A) Representative coronal brain sections stained with 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) solution from animals treated with saline control, SOD-Sol, or SOD-NPs. Dark colored regions in the TTC-stained sections indicate nonischemic areas; pale-colored regions indicate ischemic portions of the brain. B) Bar graph showing neurological severity score. Lower scores represent better neurological recovery. Control is saline control at 6 h following reperfusion. Data are shown as means ± SE. C) Survival of animals treated with SOD-NPs compared with saline control. All animals treated with saline only died within 3 d, whereas more than 75% of the animals treated with SOD-NPs not only survived but showed improvement in neurological recovery with time (*P=0.06 at 28 d compared to 6 h). Figure reproduced with permission from Ref [57].