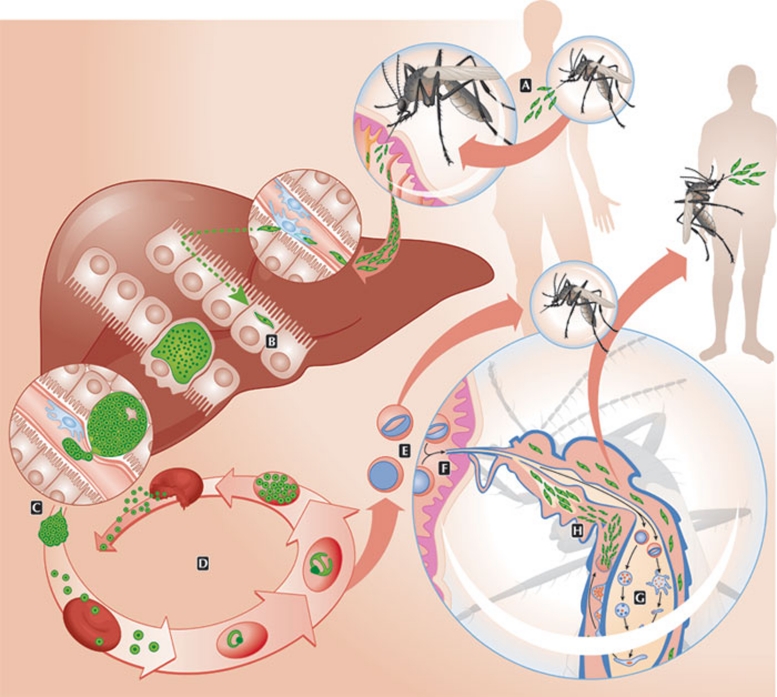
Figure 1.
Plasmodium life cycle. (A) During a blood meal, an anopheline mosquito injects Plasmodium sporozoites into the host dermis. (B) After reaching a blood vessel, sporozoites travel to the liver where—after traversing several hepatocytes—they invade a final one. (C) After asexual replication and development inside the hepatocyte, merozoites are released into the bloodstream. (D) Merozoites infect red blood cells during cycles of asexual replication. (E) Occasionally, replication cycles originate female and male gametocytes. (F) Through another blood meal, a mosquito ingests gametocytes into its midgut. (G) Fertilization of gametes occurs in the mosquito midgut with the formation of ookinetes and later the oocysts. (H) Sporozoites released from the oocyst migrate to the salivary gland of the mosquito and are released during the next blood meal.