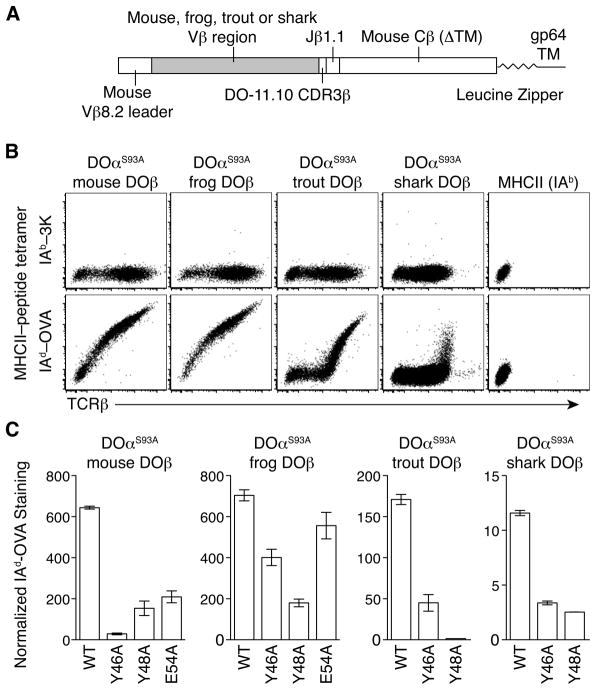
Figure 3. TCRs containing mouse, frog, trout, and shark V β bind mouse MHCII using conserved Vβ CDR2 amino acids.
A. Schematic of chimeric TCRβ construction replacing mouse Vβ8.2 with frog, trout, and shark Vβ in the DO-11.10 TCRβ for expression in insect cells. The mouse TCRβ constant region was truncated just before the transmembrane domain (ΔTM) and linked to a leucine zipper and baculovirus gp64 protein transmembrane (TM) domain. B. IAb-3K or IAd-OVA tetramer staining and TCRβ expression on SF9 insect cells expressing DOαS93A plus mouse DOβ, frog DOβ, trout DOβ, or shark DOβ compared with SF9 cells expressing surface-bound MHCII IAb plus linked 3K peptide. Plots are gated on live cells and are representative of at least 2 independent experiments. C. Geometric mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) of normalized IAd-OVA tetramer staining on SF9 insect cells expressing DOαS93A plus wild-type (WT) mouse DOβ, frog DOβ, trout DOβ, or shark DOβ and indicated CDR2β amino acid Ala-substitutions. Tetramer staining was normalized by dividing gMFI of IAd-OVA staining by gMFI of background IAb-3K staining from a narrow gate of TCR expression. Data are mean ± range from 2 independent experiments.