Fig. 1.
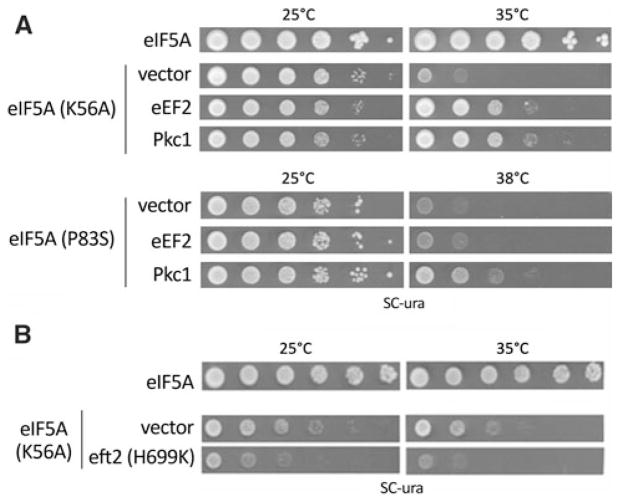
Genetic interactions between eIF5A and eEF2. a Tenfold serial dilutions of wild type (eIF5A) cells harboring the vector alone, the mutant strains eIF5AK56A or eIF5AP83S harboring the vector alone, or high-copy eEF2 or high-copy Pkc1 plasmid were plated onto SC-ura to determine the growth at permissive (25°C) or non-permissive temperatures (35°C to eIF5AK56A and 38°C to eIF5AP83S). b The wild type strain harboring the vector alone or the eIF5AK56A mutant strain harboring the vector alone or together with eEF2H699K dominant negative mutant plasmid were assayed as described in (a). The plates were photographed after 3–4 days of growth