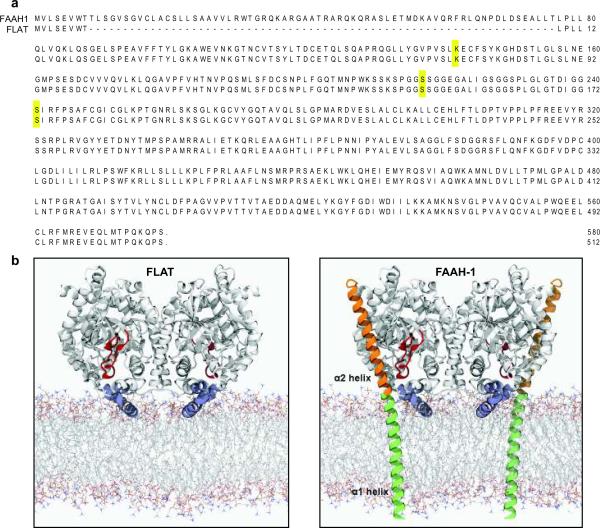
Fig. 1.
Structural properties of FLAT. (a) Predicted amino acid sequences of FLAT and FAAH-1; residues comprising the catalytic triad of FAAH-1 (Lys142, Ser217 and nucleophile Ser241) are highlighted. (b) Model of rat FLAT (left) based on the structure of FAAH-ΔTM (right), a FAAH-1 mutant lacking the α1 helix15 which is redrawn in green for illustration purposes. Most of the α1 helix and the entire α2 helix (orange) of FAAH-1 are absent in FLAT. Both FAAH-1 and FLAT contain a membrane-binding domain (blue, FLAT residues 343–367) and an 'α2-interacting loop' (red, FLAT residues 187–210), which may interact with the α2 helix and help shield the enzyme's catalytic pocket from water. The membrane model was generated using Molecular Dynamics simulations of a 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphorylcholine bilayer39.