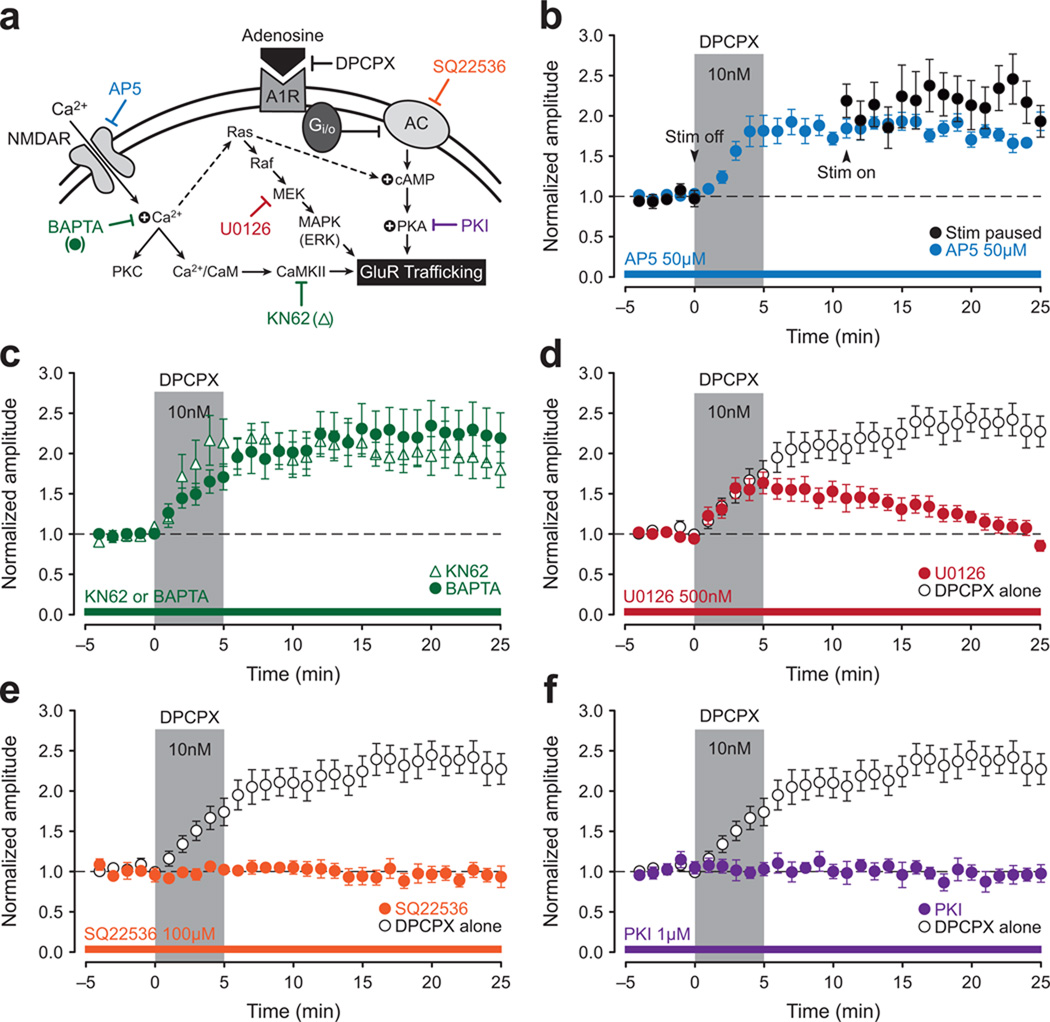
Figure 3. A1R-potentiation at CA2 synapses is mediated by cAMP-dependent activation of PKA.
A schematic overview of a likely mechanism for A1R-P in CA2 (a). Attempts to induce A1R-P in CA2 neurons were made using DPCPX (10 nM, 5-min, gray bar, b–f), and open circles, where present, show the DPCPX response in the absence of any other manipulation. A temporary pause in delivery of test stimulation at the start of DPCPX application (black circles; b) or bath application of AP5 (50 µM, blue circles; b) fails to block A1R-P. Loading cells with BAPTA (10 mM, green circles) or bath application of the CaMKII inhibitor KN62 (10 µM, open triangles) also fails to block A1R-P (c). Although the MEK inhibitor U0126 did not block induction of A1R-P (500 nM, red circles; d), it did block its consolidation. Loading cells with the adenylyl cyclase inhibitor SQ22536 (100 µM, orange circles; e) or the PKA inhibitor PKI (1 µM, purple circles; f) blocks A1R-P in CA2.