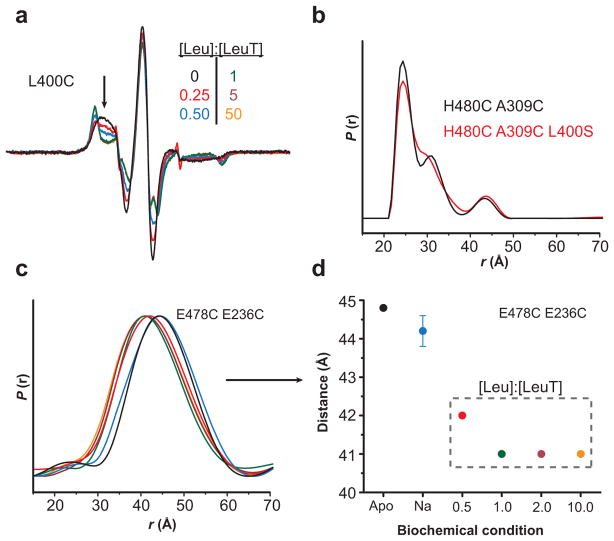
Figure 5.
Leu binding to the S1 site is the primary determinant of Leu-dependent conformational changes. (a) The decrease in spin label mobility at L400C was dependent on the [Leu]. The Leu titration of LeuT-L400C indicated a maximum change in EPR lineshape (arrow) at a 1:1 molar ratio of Leu-to-LeuT. Because the L400C mutation disrupts binding to the S2 site23, these spectral changes result from binding in the S1 site. (b) The distance distributions of LeuT-H480C/A309C (2:1 Leu-to-LeuT stoichiometry) and –H480C/A309C/L400S (1:1 stoichiometry) are superimposable, suggesting that the Leu-dependent change in distance is due to Leu occupancy in the S1 site. (c–d) The change in distance between LeuT-E478C/E236C (2:1 stoichiometry) is saturated at a 1:1 ratio, consistent with S1-driven conformational changes. The distances in (d) were obtained from the peak probability of the distance distributions in (c).