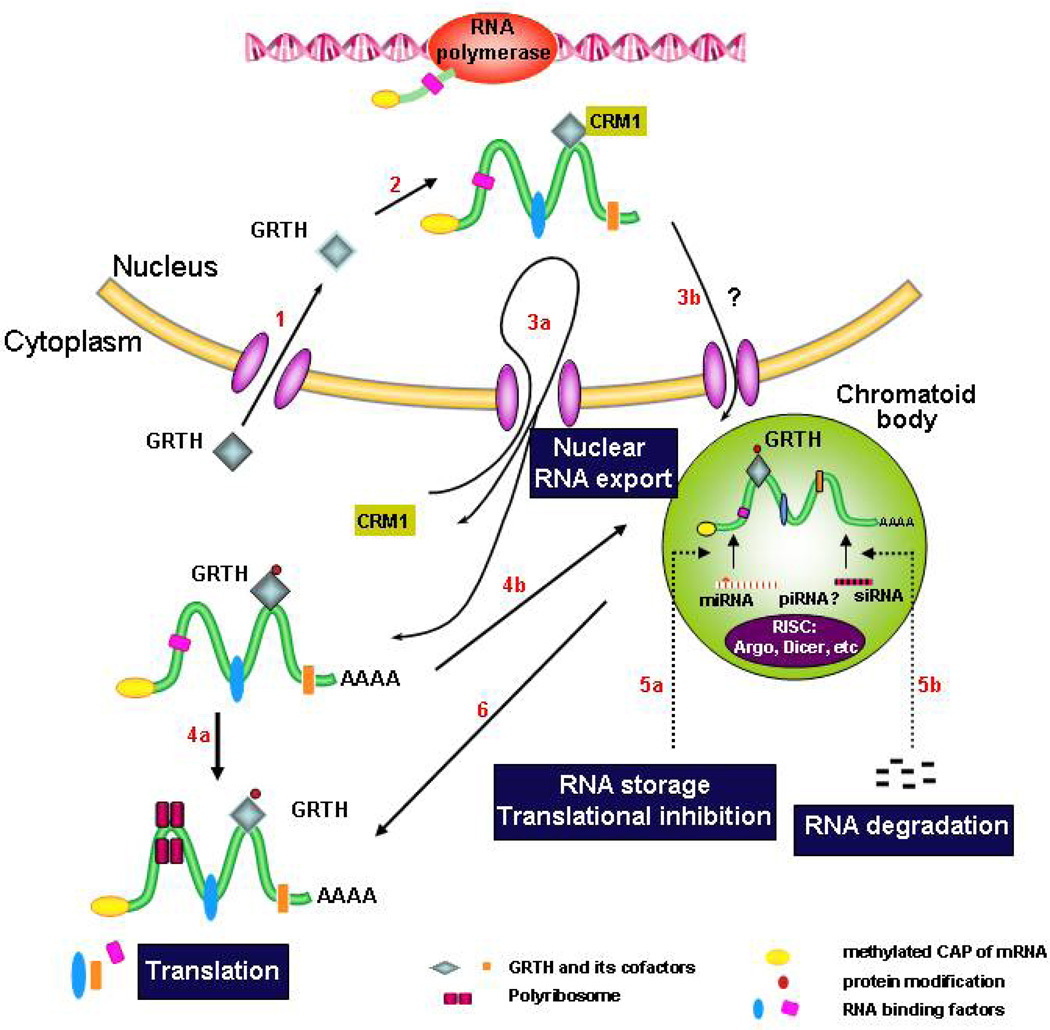
Fig. 2. Model of GRTH action in male germ cells during development.
Route 1–6 (in red) represent functions and transit of GRTH protein entry to the nucleous (1) where it binds messages and associates with CRM-1 (2), and as integral component of RNP exports messages through nuclear pores via CRM1-pathway to the cytoplasm (3a) and to the CB (3b & 4b) either directly (via nuclear pores adjacent or associated with the CB) (3b), or indirectly via the cytoplasmic route (4b). It is phosphorylated at cytoplasmic sites to deliver messages, associates to polyribosomes (4a) and participate in translation. In the CB, messages are potentially regulated via si/mi/pi RNA pathway (RNA storage and degradation) (5a & b). Stored messages are subsequently translated in polyribosomes (4a & 6).