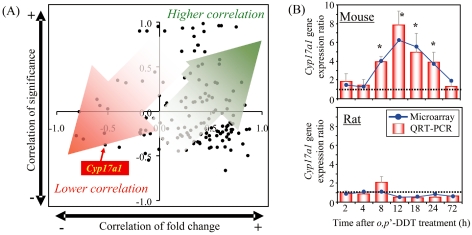
Fig. 6.
Species-specific regulation of the hepatic Cyp17a1 gene elicited by o,p’-DDT. Correlation analysis between mice and rats was performed using differentially expressed orthologous genes in the liver elicited by o,p’-DDT. The temporal profiles of the o,p’-DDT-treated mouse liver198 and those of the o,p’-DDT-treated rat liver199 were compared by determining the Pearson’s correlation of the temporal gene expression (fold change) and significance (p1[t] value by empirical Bayesian analysis) between orthologs, and the results of this comparison are presented as a scatter plot. Correlations of gene expression and significance approaching 1.0 indicate that the behaviors of the orthologous genes are similar and would fall within the upper right quadrant. (A) Orthologs tended to localize in the upper- or lower-right quadrants, indicating that the temporal gene expression changes for o,p’-DDT-treated mouse and rat liver are comparable. However, poor correlations between the temporal p1(t) values and gene expression fold changes would fall within the lower left quadrant. Cyp17a1, one of the poor-correlation genes, fell into this quadrant, suggesting that significant differences exist between the rat and mouse othologue expression profiles. (B) The hepatic Cyp17a1 gene expression levels following o,p’-DDT treatment were compared between rats and mice by QRT-PCR. Significant species-specific regulation of hepatic CYP17a1 gene was observed. * P < 0.05 by a two-way ANOVA followed by pairwise comparisons using Tukey’s test.