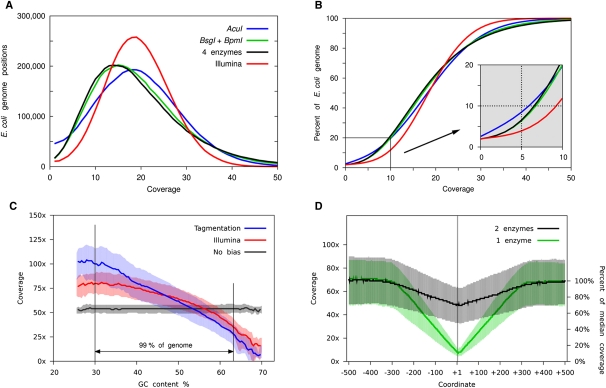
Figure 2.
Analysis of bias in 10-pg level libraries. (A,B) 1 × 106 non-redundant, uniquely mapping, high-quality, paired-end reads were randomly selected for further analysis of the Illumina library (red; 1 μg input) and each tagmented library. Tagmented libraries used 10 pg of input (blue; single enzyme—AcuI), 20 pg of input (black; two enzymes—BsgI and BpmI), and 40 pg of input (green; four enzymes—AcuI, BsgI, BpmI, and BpuEI). Coverage depth across the genome and percentage of genome covered at increasing cumulative coverage depths for each library were compared. (C) Median coverage depth for genomic regions defined by GC content was also analyzed for a single enzyme tagmentation library AcuI (blue), an Illumina library (red), and 1 × 106 size-matched fragments randomly selected in silico from the reference genome to model coverage in a non-biased manner (black). Shaded regions represent 25th and 75th inner quartile regions for each data set. The region between vertical black lines represents 99% of the total reference genome. (D) Fold coverage across 1-kb genomic regions containing endogenous cleavage sites for single enzyme (green; AcuI, AcuI sites shown) and two enzyme (black; BsgI and BpmI; BpmI sites shown) tagmented libraries. Approximately 3000 genomic regions are represented in each analysis. Absolute coverage and percentage median coverage by base position are shown for each region.